Case 4
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
A 34-year-old woman with flank pain and fever.
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
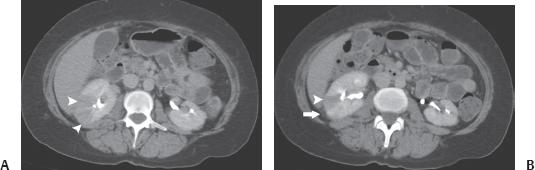
Contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) images of the abdomen at the level of the kidneys obtained during the excretory phase. (A) The right kidney is enlarged and shows randomly scattered wedge-shaped areas of mildly decreased perfusion (arrowheads in A and B). These areas involve the entire thickness of the renal parenchyma from the renal sinus to the cortical surface. (B) Perinephric stranding is present (arrow). No fluid collection is seen in the renal parenchyma or perinephric space. The renal outlines are normal. There is no hydronephrosis.
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Acute pyelonephritis: The characteristic finding is unilateral or bilateral renal enlargement with areas of mildly decreased perfusion. These areas are randomly scattered and involve the parenchyma from the renal sinus to the cortical surface.
• Renal infarcts: Multiple renal infarcts also have the appearance of perfusion defects involving the entire parenchyma and may mimic acute pyelonephritis. However, the perfusion defects due to infarcts are well defined and larger, with a complete absence of perfusion. If necessary, delayed repeat scanning can be performed, which will show no contrast accumulation in the perfusion defects, whereas in acute pyelonephritis, these areas will become denser. In subacute or chronic cases, the affected kidney is smaller.
• Delayed nephrogram from ureteric obstruction:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


