 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
A 2-month-old presents with jaundice and elevated direct bilirubin levels.
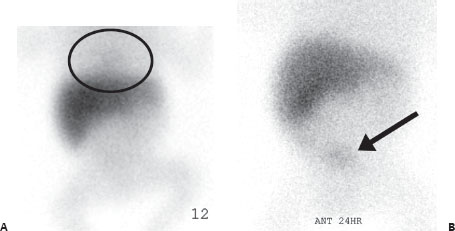
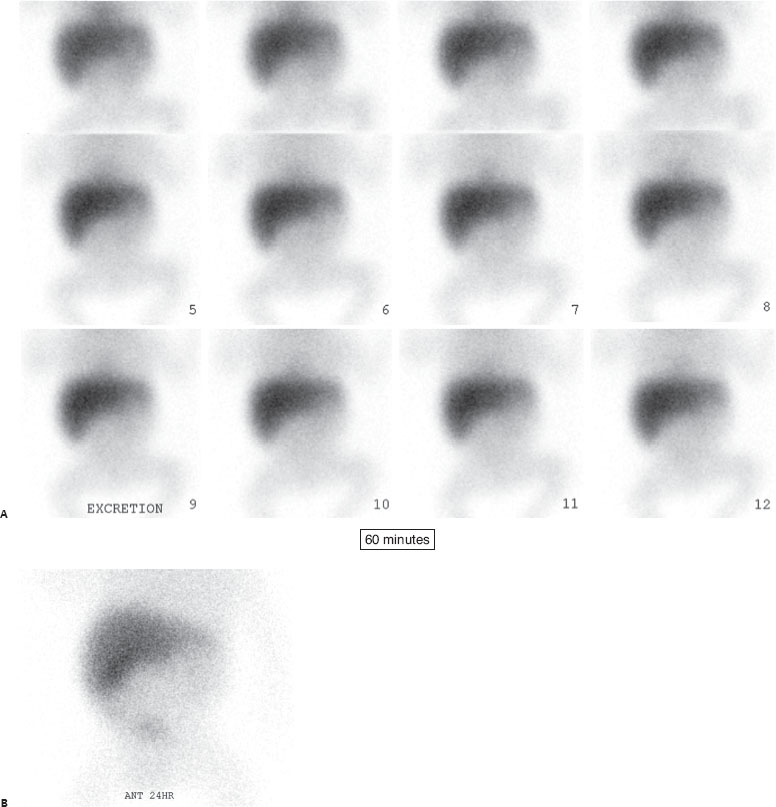
(A) Anterior images from a Tc99m-HIDA scan reveals prompt uptake of radiopharmaceutical into the liver. There is no evidence of biliary excretion after 1 hour. There is only mildly delayed blood pool clearance that can be faintly seen at 1 hour in the cardiac chambers (circle). (B) Twenty-four–hour delayed images reveal persistent uptake in the liver without any biliary excretion into bowel. Blood pool activity has cleared. Vicarious excretion of the radiopharmaceutical through the kidneys into the bladder is noted (arrow).
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
• Biliary atresia: Lack of any bowel activity, even at 24 hours, makes this the diagnosis of exclusion.
• Neonatal hepatitis: This will typically show some bowel activity by 24 hours, although it occasionally may not, if severe. It usually has more persistent blood pool activity (and the more the persistent the blood pool activity, the greater the severity of hepatic dysfunction).
• Intrahepatic cholestasis: Cholestasis can be caused by other disease processes, such as Alagille syndrome (nonsyndromic bile duct paucity) or α1
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree