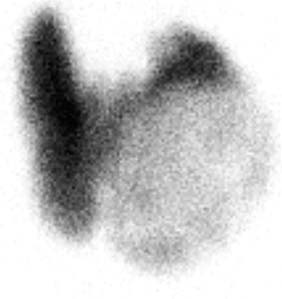
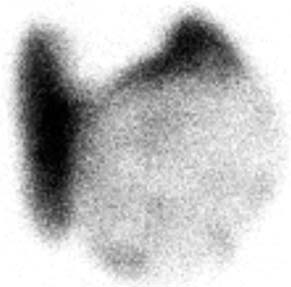
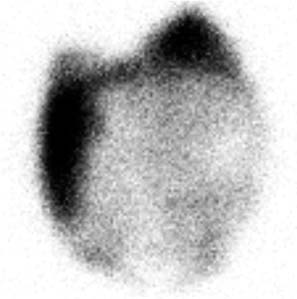
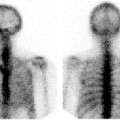
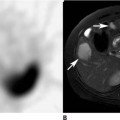
CASE 57 A 46-year-old woman presents with a very large palpable mass in the left thyroid lobe and markedly abnormal thyroid function test values: • Thyrotropin (thyroid-stimulating hormone [TSH]), < 0.01 μU/mL (normal range, 0.5–6.0 μU/mL) • Serum thyroxine (T4), 25.4 μg/dL (normal range, 4.6–12.0 μg/dL) • Serum triiodothyronine (T3), 1087 ng/dL (normal range, 80–180 ng/dL) • Thyroid peroxidase (TPO) antibodies, negative Fig. 57.1 Right anterior oblique pinhole collimator view, 123I. Fig. 57.2 Anterior pinhole collimator view, 123I. Fig. 57.3 Left anterior oblique pinhole collimator view, 123I. • 0.500 mCi of 123I administered orally 24 hours before uptake and scan • Five-minute pinhole collimator images in right anterior oblique, anterior, and left anterior oblique projections • Appropriately shielded sodium iodide thyroid probe positioned with the crystal surface 25 cm from the surface being measured. Obtain counts of the following for 2 minutes: • Calculate the iodine uptake with the following formula: The 24-hour uptake measures 85% by thyroid probe. The uptake of 85% at 24 hours is markedly increased (expected range, 15–30%). Three views (Figs. 57.1, 57.2, and 57.3) demonstrate a large, well-defined “cold” nodule in the left lobe of the thyroid gland, corresponding to the palpated nodule, within an otherwise diffusely enlarged but homogeneous gland. (Two coexisting thyroid conditions) • For the right lobe and left upper lobe, Graves disease • In the left lower lobe, primary malignant neoplasm or metastasis versus a benign condition (eg, abscess, adenoma, adenomatous hyperplasia, colloid cyst, hematoma, lymphocytic thyroiditis, parathyroid adenoma) 1. Graves disease (presumptive)
Clinical Presentation
Technique
 Thyroid bed
Thyroid bed
 Thigh (body background)
Thigh (body background)
 Room background
Room background
 Pill standard (in a neck phantom)
Pill standard (in a neck phantom)
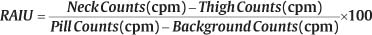
Image Interpretation
Differential Diagnosis
Diagnosis and Clinical Follow-Up
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree