CASE 58
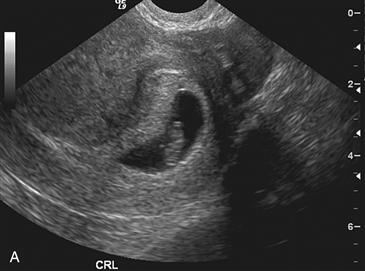
CRL = crown rump links.
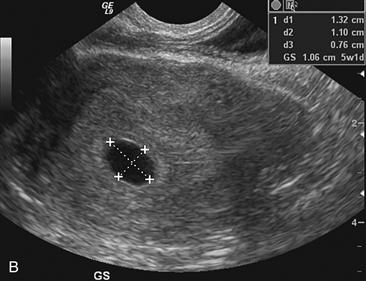
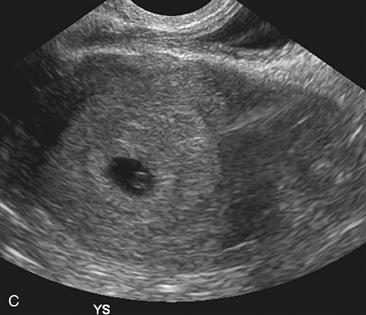
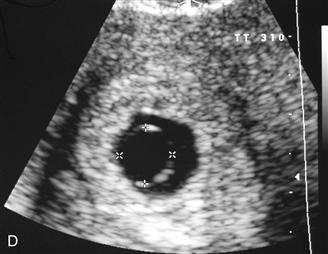
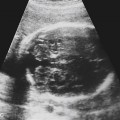
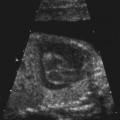
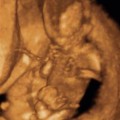
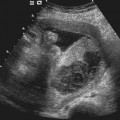
History: A patient with a positive beta–human chorionic gonadotropin (β-hCG) and pelvic pain presents to be examined for the presence of a normal gestational sac.
1. What criteria are used to aid in distinguishing a normal intrauterine pregnancy (IUP) from an abnormal one? (Choose all that apply.)
B. A yolk sac should be visible when the MSD seen on transvaginal ultrasound is 25 mm or more.
C. Fetal heart motion is usually detected when the fetal pole is equal to or greater than 2 mm.
2. What does the most recent data suggest about the use of an absolute isolated quantitative beta hCG to determine the timing of the appearance of a gestational sac in the uterus on transvaginal ultrasound?
B. 1000 mIU/mL is the threshold to see a gestational sac.
C. 5000 mIU/mL is the threshold to see a gestational sac in the uterus.
D. 10,000 mIU/mL is the new threshold to see a gestational sac in the uterus.
3. What is the significance of an abnormal or absent yolk sac?
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree