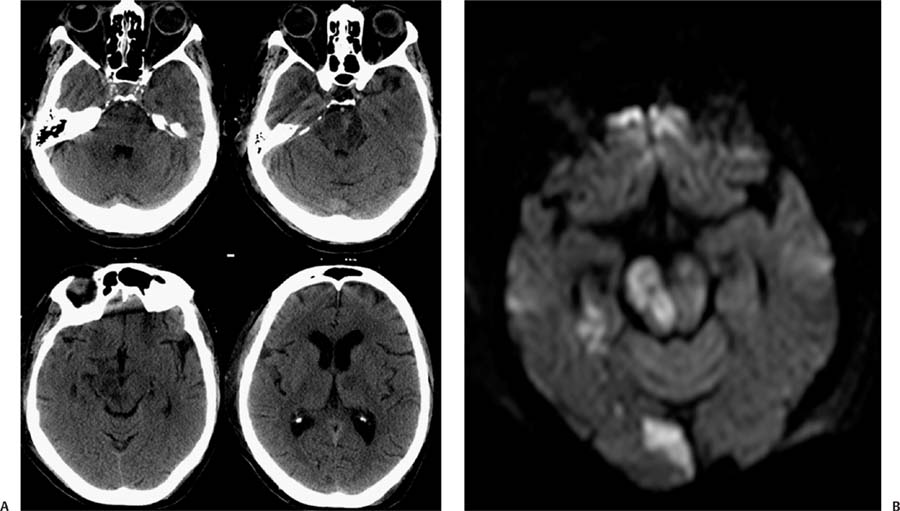
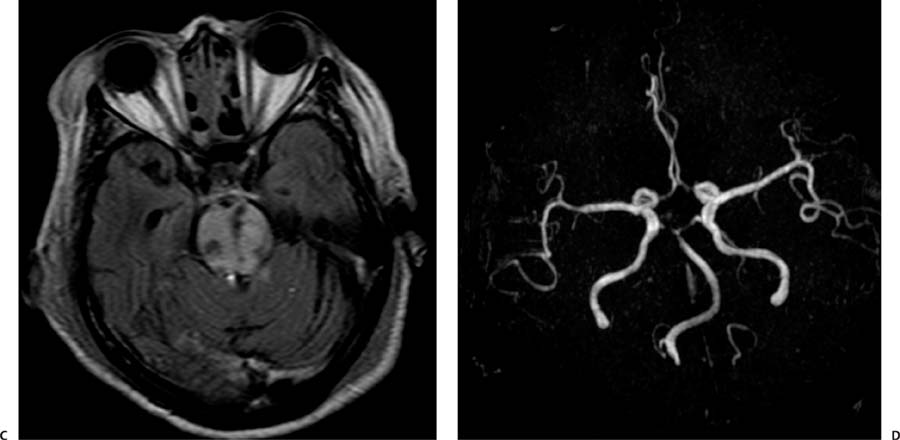
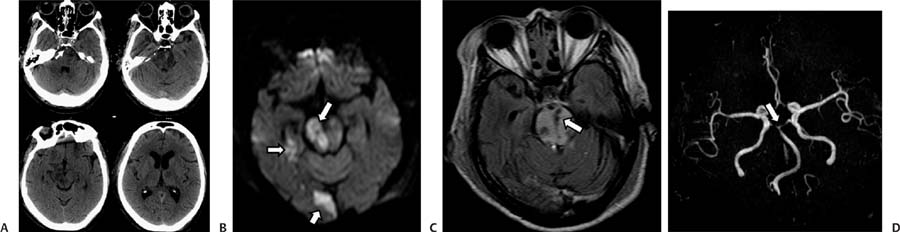
Case 61 A 70-year-old woman presenting with syncope after a fall. (A) Computed tomography (CT) of the brain shows areas of low attenuation in the pons, right cerebral peduncle, and left thalamus. Note the increased attenuation of the basilar artery (arrow). (B) Diffusion-weighted image shows restricted diffusion in the right side of the pons, right medial temporal lobe, and right occipital lobe (arrows). All the areas of hypoattenuation on the CT scan demonstrate restriction (not all of them shown). (C) Fluid-attenuated inversion recovery image through the pons shows increased signal and punctate areas of hemorrhage (arrow). (D) Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) of the brain shows no flow-related signal in the basilar tip or proximal posterior cerebral arteries (arrow). The superior cerebellar arteries are irregular and narrow. • Basilar artery thrombosis with acute posterior circulation stroke: Acute ischemic changes involve variable extensions of the brainstem, cerebellum, thalami, and temporal and occipital lobes. Edema in the posterior fossa may result in obliteration of the 4th ventricle and acute hydrocephalus.
Clinical Presentation
Further Work-up
Imaging Findings
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree