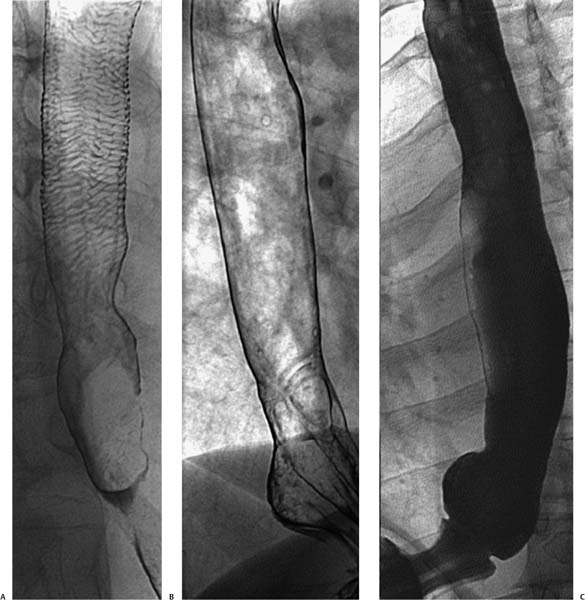
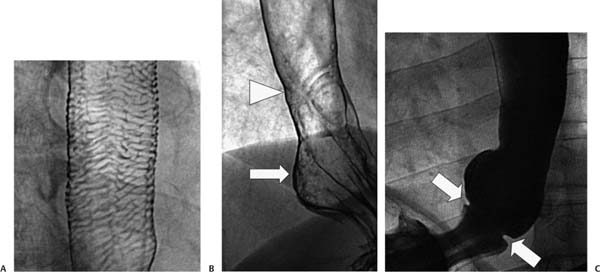
Case 67 Three different men in their mid-30s present with dysphagia and chest pain. What is the clinical significance of each diagnosis? (A) Double-contrast esophagogram shows a lattice of horizontal lines throughout the esophageal mucosa, indicating feline esophagus. (B) Double-contrast esophagogram shows a focus of transverse lines (arrowhead) a few centimeters above the gastroesophageal junction, indicating a peptic stricture from reflux esophagitis and a small hiatal hernia (arrow). (C) Single-contrast esophagogram shows a narrow horizontal ring (arrows) at the distal esophagus just above a small hiatal hernia, indicating a B ring. • Benign transverse esophageal folds: No differential diagnosis is necessary because a single diagnosis can be assigned to each case based on classic imaging findings.
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


