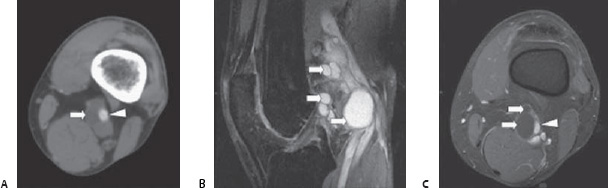
Case 92 A 45-year-old nonsmoker presents with rapidly progressing unilateral, intermittent claudication. On physical examination, a loss of the distal pulses is noted during knee flexion. (A) Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomographic (CT) scan shows nonenhancing structure (arrow) adjacent to the popliteal artery (arrowhead). (B) Sagittal, proton density, fat saturation magnetic resonance image (MRI) shows ovoid, hyperintense structures (arrows) in the popliteal fossa. (C) Axial, fast spoiled gradient echo MRI shows ovoid structures with low signal intensity (arrows) partially compressing the popliteal artery (arrowhead).
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


