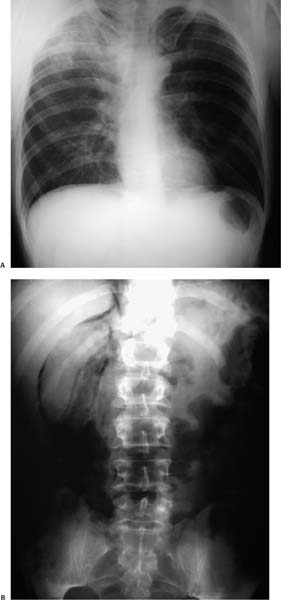
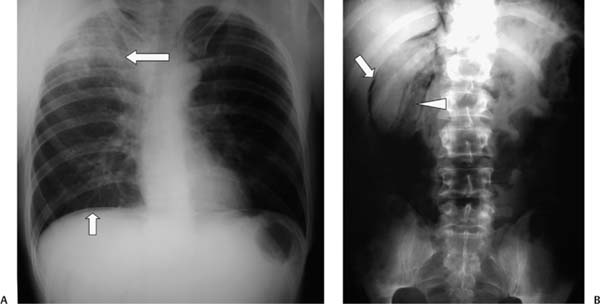
Case 99 A 25-year-old man is found unconscious on the ground and taken to the emergency department. (A) Upright abdominal radiograph shows pneumoperitoneum manifesting as a thin rim of subdiaphragmatic gas (small arrow). A presumed pulmonary contusion is visible (large arrow). (B) Abdominal radiograph shows a bubbly gas collection in the perirenal space (arrowhead), extending along the inferior margin of the liver (arrow). • Traumatic duodenal rupture: This is the most likely diagnosis, given the combination of retroperitoneal gas and pneumoperitoneum. The presumed pulmonary contusion supports the diagnosis by providing evidence of trauma. • Duodenal rupture from peptic ulcer disease or neoplasm: This can produce identical findings, but the pulmonary finding makes this less likely (see also below).
 Clinical Presentation
Clinical Presentation
 Imaging Findings
Imaging Findings
 Differential Diagnosis
Differential Diagnosis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


