KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Hernia: Weakness or defect in fibromuscular wall with protrusion of organ or tissue through defect
Imaging
- •
Midline hernias
- ○
Epigastric: Between xiphisternum and umbilicus
- ○
Umbilical: Umbilical or immediate paraumbilical region
- ○
Hypogastric: Between umbilicus and pubic symphysis
- ○
- •
Lateral hernias
- ○
Spigelian
- ○
Lumbar: Occur in 2 potentially weak areas of flank
- ○
- •
Incisional hernia: Located at surgical incisional site
- •
Ultrasound 1st-line imaging for smaller hernias or children
- ○
Dynamic, real-time examination; using maneuvers such as Valsalva or standing position to improve detection
- ○
- •
CT for larger, deep-seated hernias and complications and obese patients
- •
Localize site/size of abdominal wall defect and content
- ○
Bowel: “Target” echo pattern with visible peristalsis
- ○
Omental fat: Echogenic/hypoechoic nonperistalsing
- ○
- •
Document with cine clips
- •
Complications: Incarceration, strangulation, bowel obstruction
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Abdominal wall tumor
- •
Abdominal wall abscess or seroma
- •
Abdominal wall or rectus sheath hematoma
- •
Divarication (diastasis) of rectus abdominis muscles
Clinical Issues
- •
Most common abdominal wall lesion seen in ultrasound practice; discomfort, pain, intermittent intestinal obstruction
- •
Reducible/enlarging abdominal wall swelling
- •
20% require emergency repair for incarceration and strangulation
Scanning Tips
- •
High-resolution linear transducer for abdominal wall; curvilinear lower frequency and extended field of view (panoramic) for diastasis recti/large hernias/overview
 arising from around the umbilicus. The locations of epigastric
arising from around the umbilicus. The locations of epigastric  , spigelian
, spigelian  , and hypogastric
, and hypogastric  hernias are also shown for reference.
hernias are also shown for reference.
 at the superior aspect of the umbilicus.
at the superior aspect of the umbilicus.
 protrudes through a narrow defect
protrudes through a narrow defect  in the linea alba, accentuated by the Valsalva maneuver.
in the linea alba, accentuated by the Valsalva maneuver.
 with a small defect
with a small defect  . No color flow is seen in the herniated omentum
. No color flow is seen in the herniated omentum  , not necessarily indicative of strangulation, as fat is usually hypovascular.
, not necessarily indicative of strangulation, as fat is usually hypovascular.
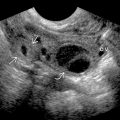
 containing ascites, which protrudes through a defect in the linea alba at the umbilicus
containing ascites, which protrudes through a defect in the linea alba at the umbilicus  . No bowel is seen in the hernia.
. No bowel is seen in the hernia.
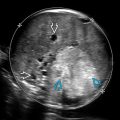
 is shown. Due to its size, the hernia was imaged with a curvilinear transducer. The defect in the abdominal wall is still visualized
is shown. Due to its size, the hernia was imaged with a curvilinear transducer. The defect in the abdominal wall is still visualized  .
.