| Skull Base Region | Sella turcica |
| Histopathology | Cushing disease |
| Prior Surgical Resection | Yes |
| Pertinent Laboratory Findings |
|
Case description
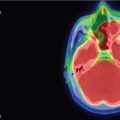
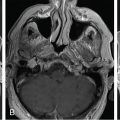
A 36-year-old woman with new-onset vision changes was diagnosed with central serous retinopathy by her ophthalmologist and treated with laser therapy. When her symptoms returned, she sought a second opinion, which prompted measurements of the pituitary hormones. Her 24-hour urinary-free cortisol levels were elevated up to 142 mcg/24 h. Two 1-mg dexamethasone suppression tests failed to suppress her serum cortisol, although an 8-gram overnight dexamethasone suppression test did result in appropriate cortisol suppression. Inferior petrosal sinus sampling confirmed a pituitary etiology and a 3T MRI revealed a 6 mm × 5 mm adenoma in the right anterior pituitary gland ( Figure 3.13.1 ).

At that time, she was complaining of fatigue, anxiety, easy bruising, and hair thinning, in addition to vision changes. The decision was made to pursue transsphenoidal resection. During surgery, no discrete tumor was visualized, but two suspicious areas were removed, leaving between 30% and 40% of the anterior lobe behind. Surgical pathology showed no definite adenoma but identified Crooke hyaline changes, indicating excess adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) secretion. Her symptoms resolved by postoperative day 4, and morning cortisol and ACTH levels dropped to within normal limits at 1.9 mcg/dL and <5 pg/mL, respectively. Thus, she was diagnosed with pathology-negative Cushing disease (CD).
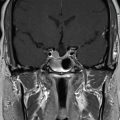
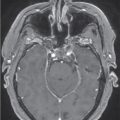
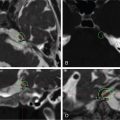
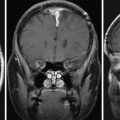
The patient remained symptom-free for 2 years postoperatively, but then noticed a recurrence of vision deficits as well as fatigue, easy bruising, anxiety, and difficulty sleeping. An endocrine workup showed elevated 24-hour urinary-free cortisol to 92 mcg/24 h. MRI showed no evidence of focal mass ( Figure 3.13.2 ). Therefore, the decision was made to pursue Gamma Knife Radiosurgery (GKRS) treatment for the remaining gland ( Figure 3.13.3 ).
| Radiosurgery Machine | Gamma knife |
| Radiosurgery Dose (Gy) | 24, at 50% isodose line |
| Number of Fractions | 1 |


| Critical Structure | Dose Tolerance |
|---|---|
| Optic nerve/chiasm |
|
| Brainstem |
|
| Cranial nerves in cavernous sinus |
|
| Cavernous carotid artery |
|
| Normal pituitary gland and pituitary stalk | Recommend limiting radiation exposure to the identifiable gland to <11.0 Gy and avoid whole-sella SRS whenever possible |
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree