KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Inflammation of liver due to viral infection or toxic agents
Imaging
- •
Acute: Enlarged liver
- •
Chronic: Decrease in liver size
- •
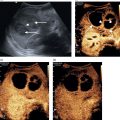
Grayscale ultrasound
- ○
Acute hepatitis: Hepatomegaly and diffusely hypoechoic parenchyma (variably seen)
- ○
Steatohepatitis and acute alcoholic hepatitis: Hepatomegaly and diffusely hyperechoic liver parenchyma
- ○
Thickening of gallbladder wall
- –
Most pronounced in acute hepatitis A
- –
- ○
Starry-sky appearance: Portal triads appear markedly echogenic due to periportal edema against background hypoechoic liver (variably seen)
- –
May be related to periportal edema
- –
- ○
- •
Pulsed Doppler ultrasound
- ○
Elevated hepatic arterial velocity
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Infiltrative hepatocellular carcinoma
- •
Lymphoma
- •
Steatosis (fatty liver)
Pathology
- •
Viral hepatitis: Caused by 1 of 5 viral agents
- ○
Hepatitis A (HAV), B (HBV), C (HCV), D (HDV), E (HEV) viruses
- ○
- •
Alcohol abuse
- •
Autoimmune reactions
- •
Metabolic disturbances
- •
Toxic or drug-induced injury
- •
Exposure to environmental agents
- •
Radiation therapy
Scanning Tips
- •
Check for tender liver, which may be related to inflammation from acute hepatitis
- •
Check gain settings, which can affect appearance of liver and may mimic hepatitis or steatosis