KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Benign, solid paratesticular tumor of mesenchymal origin
Imaging
- •
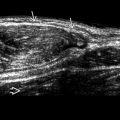
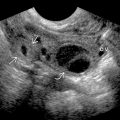
Solid intrascrotal mass, usually extratesticular
- •
Rounded or oval, well circumscribed, varying echogenicity
- •
Size: 5 mm to 5 cm
- •
Hypovascular or avascular on color Doppler US
- •
Location
- ○
Epididymis: Most common location overall
- ○
May arise in tunica albuginea
- ○
Rarely intratesticular or other locations, such as spermatic cord and prostate
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Leiomyoma
- •
Lipoma
- •
Cystadenoma
Clinical Issues
- •
Most common solid mass in epididymis
- ○
36% of all paratesticular tumors
- ○
- •
Slowly enlarges over years
- •
Most surgically excised to confirm diagnosis
- •
Some urologists and patients elect surveillance
- •
Age: 20 years and older
- ○
Mean: 36 years
- ○
Rarely seen in boys
- ○
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Consider leiomyoma
Scanning Tips
- •
Gentle transducer pressure may show mass can move independently of testis
- •
Small adenomatoid tumors of epididymis may be easily missed and, therefore, full visualization of head, body, and tail of epididymis is important on all routine scrotal exams