Smallest paired organ in suprarenal location in the abdomen.
Weighs ~4 grams each in the normal nonstressed adult.
Though CT is a better imaging modality, USG may be helpful depending on the operator experience, patient’s body habitus, and type of equipment.
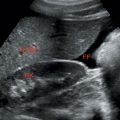
In the neonatal period, normal adrenal gland can be visualized readily because of its relatively large size and little perirenal fat.
V/Y/Z shaped.
Long linear structure lying flat (Lying down sign in patients with renal agenesis).
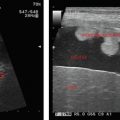
Tuberculosis and histoplasmosis—Bilateral, diffuse enlargement, heterogeneous echotexture with calcifications.
HIV+ patient’s demonstrate heterogeneously hypoechoic masses, may contain gas.
Adrenal abscess—common in neonates.
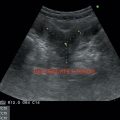
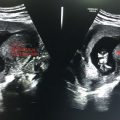
On USG
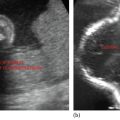
• Solid, small, round well-defined lesions in suprarenal region (Figure 8.1)
• In a parasagittal plane, if RUQ retroperitoneal fat stripe is displaced
Posteriorly
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree