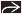Ampullary Carcinoma
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Amir A. Borhani, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial neoplasm (adenocarcinoma) arising from ampulla of Vater
Imaging
Ampullary mass with variable attenuation (most often hypodense) distinct from pancreas with dilated CBD and PD; nodal or liver mets in advanced cases
“Double duct” sign with obstruction of common bile duct and pancreatic duct
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pancreatic head carcinoma invading ampulla
Adenoma of ampulla
Distal cholangiocarcinoma
Mesenchymal tumor of ampulla
Duodenal carcinoma (adenocarcinoma)
Pathology
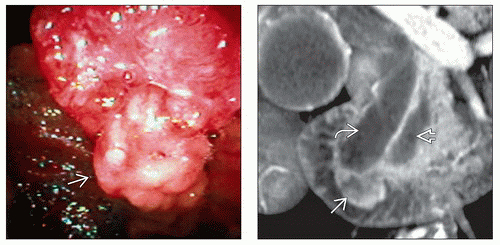
Lobulated soft tissue mass arising from ampulla of Vater
Markedly increased incidence in hereditary polyposis syndromes (e.g., familial adenomatosis coli, hereditary nonpolyposis colon cancer, etc.)
Clinical Issues
Jaundice (80%), weight loss (61%), abdominal pain, & back pain (46%) are most common symptoms
Better prognosis than periampullary carcinoma of biliary or pancreatic origin
Diagnostic Checklist
Duodenal distension with water on CECT key to identifying lesion
Perform dedicated pancreatic protocol when ampullary lesion suspected
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Malignant epithelial neoplasm (adenocarcinoma) arising from ampulla of Vater
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Soft tissue (ST) mass involving ampulla
“Double duct” sign with obstruction of both common bile duct (CBD) and pancreatic duct (PD)
Lesion best visualized on CECT when duodenum distended with water
Location
Within ampulla of Vater or overlying periampullary duodenal mucosa
Size
1-4 cm in diameter; mean 2.7 cm
Morphology
Often lobulated mass
Radiographic Findings
ERCP
Visible ampullary mass
Obstruction of CBD and PD
Useful for biopsy
Fluoroscopic Findings
Upper gastrointestinal: Filling defect in 2nd part of duodenum in region of ampulla of Vater
CT Findings
CECT
Ampullary mass with variable attenuation (most often hypodense) distinct from pancreas, with dilated CBD and PD
Nodal or liver metastases in advanced cases
MR Findings
T1WI
Hypointense to pancreas on non-fat-suppressed T1WI
T1WI FS
Isointense or slightly hypointense to pancreas on fat-suppressed T1WI
T2WI
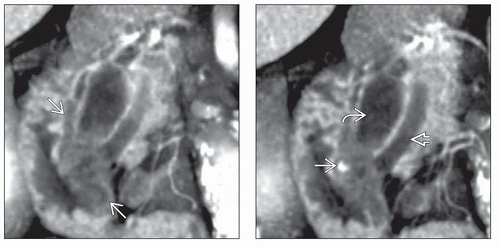
Intermediate signal ampullary mass
Dilated main PD and CBD
T1WI C+
Enhancing ST mass of lower signal than pancreas
MRCP
Dilated PD and CBD
Up to 76% accuracy
Ultrasonographic Findings
Grayscale ultrasound
Dilated CBD and PD
Ampullary mass usually not visible
Liver metastases in advanced cases
Color Doppler
No flow in dilated hypoechoic CBD and PD
Endoscopic US
Useful for staging (most accurate modality for T staging) and biopsy
Detection of nodal metastases
Angiographic Findings
Conventional
Superselective injection of gastroduodenal artery demonstrates hypovascular mass
Nuclear Medicine Findings
PET
May demonstrate liver metastases as FDG-avid lesions
Hepatobiliary scintigraphy
Dilated bile ducts
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool
CECT with dedicated biphasic pancreatic protocol or multiphasic MR with MRCP
Protocol advice
Patient to drink 16 oz of water just prior to CT
Arterial phase acquisition: Rapid bolus injection of 150 mL IV contrast (4-5 mL/s); 1.25 mm collimation after 10-second delay
Venous phase acquisition at 70 seconds; 5 mm collimation
Reconstruct pancreas images: 20 cm field of view
Additional reformations including curved planar reformat of PD and CBD useful
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pancreatic Head Carcinoma Invading Ampulla
Hypoattenuating mass on late arterial-phase CECT
Obstructed CBD and PD
Adenoma of Ampulla
Indistinguishable from carcinoma on CT
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree