Pose Model
(1)
Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, University of British Columbia (UBC), Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada
(2)
Department of Mechanical Engineering, UBC, Vancouver, BC V6T 1Z4, Canada
Abstract
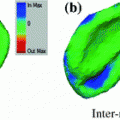
The vertebral column is of particular importance for many clinical procedures such as anesthesia or anaelgesia. One of the main challenges for diagnostic and interventional tasks at the spine is its robust and accurate segmentation. There exist a number of segmentation approaches that mostly perform segmentation on the individual vertebrae. We present a novel segmentation approach that uses statistical multi-object shape pose models and evaluate it on a standardized data set. We could achieve a mean dice coefficient of
pose models and evaluate it on a standardized data set. We could achieve a mean dice coefficient of 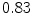 for the segmentation. The flexibility of our approach let it become valuable for the specific segmentation challenges in clinical routine.
for the segmentation. The flexibility of our approach let it become valuable for the specific segmentation challenges in clinical routine.
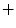 pose models and evaluate it on a standardized data set. We could achieve a mean dice coefficient of
pose models and evaluate it on a standardized data set. We could achieve a mean dice coefficient of 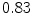 for the segmentation. The flexibility of our approach let it become valuable for the specific segmentation challenges in clinical routine.
for the segmentation. The flexibility of our approach let it become valuable for the specific segmentation challenges in clinical routine.A. Seitel and A. Rasoulian contributed equally to this work.
1 Introduction
Segmentation of the spinal column is an important task for many computer-aided diagnosis and intervention procedures. Despite the high contrast of bony structures in CT volumes, it remains challenging due to the presence of unclear boundaries, the complex structure of vertebrae, and substantial inter-subject variability of the anatomy. Most of the proposed methods for automatic or semi-automatic spine segmentation rely on an initialization step of one or multiple vertebrae followed by a separate segmentation of each vertebra [1–7]. Considering each vertebra separately, however, may result in overlapping segmentations in areas where a clear boundary is missing in the volume data. Although there exist approaches as the one of Klinder et al. [2] that e.g. penalize overlapping areas, to our knowledge there is no method that incorporates common shape variations among the vertebrae of one subject which can be of great benefit for the segmenation quality. We thus propose an approach for segmentation of the spine in CT data which is based on a statistical multi-object model which incorporates both shape and pose information of the vertebral column.
2 Methods
Our segmentation technique is based on a statistical multi-vertebrae shape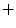 pose model which is registered to the bony edges of the spinal column as extracted from the CT volume. The basic principles of this method have previously been presented in [8, 9] and will be summarized in the following paragraphs.
pose model which is registered to the bony edges of the spinal column as extracted from the CT volume. The basic principles of this method have previously been presented in [8, 9] and will be summarized in the following paragraphs.
 pose model which is registered to the bony edges of the spinal column as extracted from the CT volume. The basic principles of this method have previously been presented in [8, 9] and will be summarized in the following paragraphs.
pose model which is registered to the bony edges of the spinal column as extracted from the CT volume. The basic principles of this method have previously been presented in [8, 9] and will be summarized in the following paragraphs.2.1 Model Construction
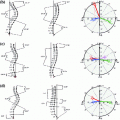
For construction of the model the idea is to analyze the pose and shape statistics separately as they are not necessarily correlated and are not formulated in the same parameter space. The model training then results in the modes of variations for both shape and pose, represented by 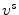 and
and 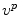 , respectively. Hence, a new instance of the model can be calculated as follows
, respectively. Hence, a new instance of the model can be calculated as follows
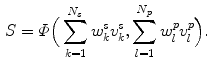
where 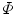 is a similarity transform,
is a similarity transform, 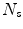 and
and 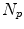 are the number of modes of variations for shape and pose, and
are the number of modes of variations for shape and pose, and 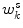 and
and 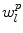 are the corresponding weights.
are the corresponding weights.
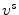 and
and 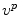 , respectively. Hence, a new instance of the model can be calculated as follows
, respectively. Hence, a new instance of the model can be calculated as follows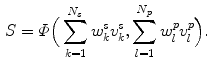
(1)
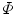 is a similarity transform,
is a similarity transform, 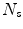 and
and 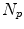 are the number of modes of variations for shape and pose, and
are the number of modes of variations for shape and pose, and 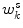 and
and 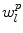 are the corresponding weights.
are the corresponding weights.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree