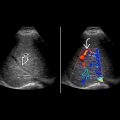
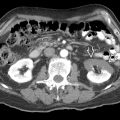
KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Distension of appendiceal lumen as result of mucin accumulation from epithelial proliferation or obstruction
Imaging
- •
Distended tubular or pear-shaped cystic structure in right lower quadrant with low-level internal echoes
- •
Connects with medial wall of cecal pole
- •
Presence of calcification in wall strongly supports diagnosis of appendicular mucocele
- •
Concentric layering of dense mucoid material gives onion skin appearance
- •
Fecalith or appendicolith may be visible in obstructive type
- •
Hypovascular
- •
Soft tissue thickening and irregularity of mucocele wall suggest malignancy
- •
Contrast-enhanced CT scan is best imaging modality for characterization and staging
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Appendiceal carcinoma or acute appendicitis
- •
Hydrosalpinx
- •
Cystic ovarian neoplasm
- •
Tuboovarian abscess
- •
Duplication cyst/mesenteric cyst
Pathology
- •
Benign > malignant
Clinical Issues
- •
Most commonly: Right lower quadrant pain/palpable mass
- •
Frequently discovered incidentally
- •
Preoperative differentiation of benign and malignant mucoceles challenging
Scanning Tips
- •
Transvaginal ultrasound improves image quality and helps to differentiate from ovarian cystic masses
 in the right pelvis, containing echogenic mucoid material.
in the right pelvis, containing echogenic mucoid material.