Biliary Metastases and Lymphoma
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
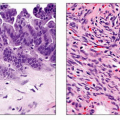
Metastatic deposits involving gallbladder (GB) or bile duct (BD) wall
Imaging
Best diagnostic clue: Polypoid GB mass > 1.5 cm in patient with known melanoma
Ultrasound for initial diagnosis
CECT or MR for global view of abdomen
Morphology
Metastases: Polypoid mass in GB wall; BD wall mass causing luminal obstruction
Lymphoma: Bulky GB & porta hepatis mass with generalized lymphadenopathy
Top Differential Diagnoses
Benign intramural gallbladder polyp
Gallbladder carcinoma
Adenomyomatosis
Pathology
Lymphoma
Most cases are non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL)
Metastases
Melanoma is most common primary tumor
Renal cell & other cancers have been reported
Clinical Issues
Most patients are asymptomatic
Lesions usually discovered as part of CT staging
RUQ pain or jaundice may result from BD metastases; rarely from lymphoma
Metastases carry poor prognosis; usually part of widespread & advanced disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree