KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Saccular outpouching from herniation of bladder mucosa and submucosa through muscular wall of bladder
Imaging
- •
Most commonly near ureterovesical junction
- •
Anechoic outpouching from bladder with narrow or wide neck, may empty with micturition
- •
CT/MR: Fluid attenuation outpouching from bladder
- •
Usually fills with contrast on excretory postcontrast phase
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Urachus
- •
Everted ureterocele
- •
Paraovarian cysts in female
- •
Pelvic cysts in male
Pathology
- •
Acquired: Most common secondary to chronic bladder outlet obstruction (60%)
- •
Congenital: Hutch diverticulum (40%)
- •
Vesicoureteral reflux
Clinical Issues
- •
Narrow-neck diverticula: Urinary stasis → complications such as infection, stone, and ureteral obstruction
- •
Secondary inflammation predisposes to development of carcinoma within diverticulum
- •
Complications
- ○
Carcinoma
- ○
Vesicoureteral reflux
- ○
Ureteral obstruction
- ○
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for debris, calculi, or solid masses in diverticula, which can indicate complication
- •
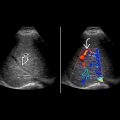
Color Doppler may show jet to and from diverticulum to bladder; do not mistake for ureteral jet
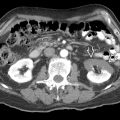
 arising from the lateral bladder wall, due to herniation of the mucosa and submucosa through the muscular wall.
arising from the lateral bladder wall, due to herniation of the mucosa and submucosa through the muscular wall.
 with narrow necks
with narrow necks  . One of the diverticula shows a urinary jet as Doppler signal into the diverticulum
. One of the diverticula shows a urinary jet as Doppler signal into the diverticulum  .
.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree