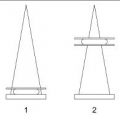
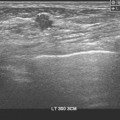
A. A
B. B
C. C
D. D
2 You are attempting a stereotactic biopsy on a patient with calcifications very close to the chest wall and difficult to image with the patient prone. What is the best option?
A. Recommend an MRI.
B. Use towels to compress the breast side to side to push the front of the breast out.
C. Retarget to get as close as possible.
D. Place the patient’s arm and shoulder through the hole in the stereotactic table.
3 You are performing an ultrasound-guided biopsy on a patient with a lesion close to the chest wall. Which of the following is the best option?
A. Roll the patient and approach at an angle so the needle is parallel to the chest wall.
B. Explain to the patient the likely risk of pneumothorax.
C. Schedule the patient for wire localization instead.
D. Aim for the periphery of the lesion.
4 Cytologic analysis should be performed for fluid removed during an ultrasound-guided cyst aspiration, if the fluid appears
A. Bright red
B. Green
C. Thick and maroon or dark brown
D. Yellow
5 What is the standard degree difference between the two stereotactic pair images obtained during stereotactic needle biopsy?
A. 20 degrees
B. 30 degrees
C. 50 degrees
D. 60 degrees
6 What is the purpose of using a spinal needle for anesthesia during a stereotatic vacuum-assisted biopsy?
A. To create a tract for the biopsy needle
B. To form the skin wheal
C. To inject beyond the area being biopsied because of the dead space of the needle distal to the sample notch
D. To reduce the burn associated with lidocaine injection
7 You recommend a breast biopsy on a patient but discover she is on aspirin. What is the next best step in management?
A. Counsel patient for increased risk of hematoma/hemorrhage.
B. Cancel biopsy and instead recommend follow-up in 6 months.
C. Stop ASA for 7 days and then biopsy.
D. Do nothing.
8 You perform a stereotactic biopsy, and specimen x-ray demonstrates the calcifications in question; however, pathology reports no calcifications seen. What do you recommend?
A. Recommend repeat biopsy.
B. Follow-up mammogram in 6 months.
C. Recommend surgical excision of the biopsy site.
D. X-ray the pathology blocks and check with polarized light for calcium oxalate.
9 The immediate subareolar area is difficult to adequately anesthetize. Which of the following is the simplest and most effective way to achieve full anesthesia of the nipple areolar complex?
A. Double the amount injected of 1% lidocaine.
B. Apply topical lidocaine to the nipple 30 minutes prior to biopsy.
C. No need to do anything additional.
D. Buffer with sodium bicarbonate.
10 When targeting a lesion for stereotactic core biopsy, images are obtained at +15 and −15 degrees. The images obtained show apparent movement of the target lesion, known as parallax shift. The distance of apparent lesion movement is used to calculate which coordinate?
A. x (horizontal)
B. y (vertical)
C. z (depth)
11 An axial CT image of a postlumpectomy patient is shown. What is the most common complication of breast surgery?
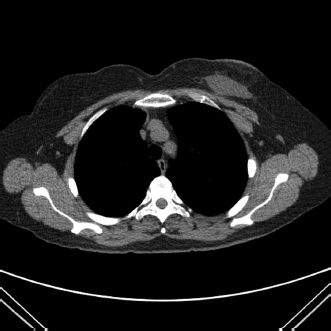
A. Abscess/infection
B. Hemorrhage
C. Lymphedema
D. Necrosis
E. Seroma
12 What is the best technique to attempt if the stereotactic needle is in the breast at the appropriate depth and the lesion is too far from it?
A. Completely withdraw the needle out of the skin and make a second skin opening.
B. Change only the z coordinate.
C. Change the x and y coordinates after retargeting the lesion.
D. Cancel the procedure.
13a A 42-year-old female presents for a screening mammogram. Thin linearbranching calcifications were noted in the left upper outer breast, new from a prior study. There is no family history of breast cancer. The patient is asymptomatic. What is the appropriate next step?
A. Clinical breast exam to detect any underlying masses
B. Stereotactic biopsy
C. Referral to surgery for excisional biopsy
D. Additional mammographic imaging
E. Short-term 6-month follow-up to assess stability
13b What is the appropriate BI-RADS category?
A. BI-RADS 0
B. BI-RADS 1
C. BI-RADS 2
D. BI-RADS 3
E. BI-RADS 4
13c After diagnostic mammogram, calcifications were noted to span a distance of 6 cm. What is the next appropriate step?
A. Refer to surgery for lumpectomy.
B. Refer to surgery for left breast mastectomy.
C. Refer to surgery for left breast mastectomy and preventative right breast mastectomy.
D. Stereotactic biopsy
14 Which one of the following patients can still be qualified for radiation therapy?
A. Patient with multicentric or diffuse disease
B. Pregnant patient
C. Patient who has had previous radiation therapy
D. Patient with collagen vascular disease
E. Patient with axillary lymphadenopathy
15 Which of the following is considered a contraindication to breast-conserving therapy (lumpectomy and radiation)?
A. Breast cancer diagnosed in the third trimester of pregnancy
B. Axillary metastases
C. Prior history of radiation and lumpectomy in the contralateral breast
D. Two or more separate tumors in different quadrants of the same breast
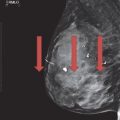
16 Stereotactic biopsy of the following calcifications was performed. Specimen radiograph confirmed that two calcifications were present in the specimens.
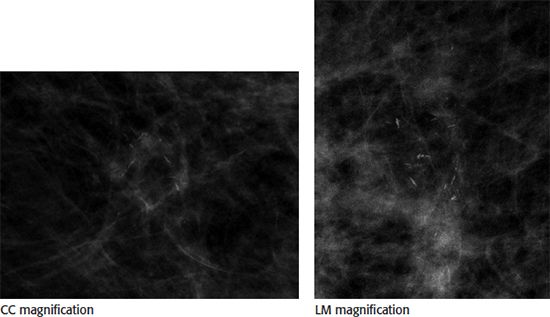
Core biopsy pathology results returned as “benign, fibrocystic changes with microcalcifications.” What is the next most appropriate step?
A. Annual screening mammogram
B. Recommendation for surgical biopsy
C. 6 month follow-up postprocedure mammogram
D. Repeat stereotactic biopsy
E. Breast MRI
17 A patient presents prior to a planned lumpectomy for wire localization of a 3-cm extent of previously biopsied, known malignant, calcifications in the left breast. The best course of action is
A. Place a wire in the center of the calcifications
B. Place a wire at one of the margins of the calcifications and provide measurements and instructions to the surgeon on what nearby tissue to excise
C. Place two wires, using the bracketing technique, at each edge of the calcifications
D. Cancel the procedure and call the surgeon, this extent of disease is too large for lumpectomy and mastectomy should be considered
18 Of the following choices, which needle biopsy device is considered most effective for use during stereotactic-guided breast biopsy of microcalcifications?
A. 14-gauge or smaller gauge spring loaded
B. 14-gauge or smaller gauge vacuum assisted
C. 11-gauge or larger gauge spring loaded
D. 11-gauge or larger gauge vacuum assisted
19 What is the most appropriate indication to perform galactography?
A. Single duct nonspontaneous and spontaneous bloody, milky, or clear nipple discharge
B. Single duct spontaneous bloody, milky, or clear nipple discharge
C. Single duct nonspontaneous and spontaneous bloody, serous, or clear nipple discharge
D. Single duct spontaneous bloody, serous, or clear nipple discharge
E. Single duct spontaneous bloody, serous, or milky nipple discharge
20 A mammographic wire localization is being performed for biopsy-proven invasive ductal carcinoma. The distance from the tip of the needle to the mass is 3 cm. Based on the image below, what is the next most appropriate step?
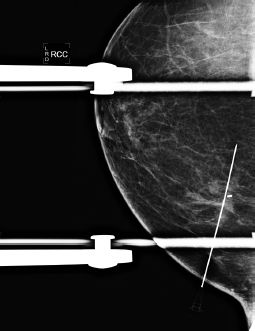
A. The patient goes to the OR; procedure is complete.
B. Return to the ML view for repositioning.
C. Retract the needle slightly, and take another image.
D. Place the wire, and take another image.
21 A specimen radiograph postwire localization was performed. A new nurse in the OR calls into the reading room with some questions. Which of the following is most accurate regarding specimen radiographs?
A. Routinely performed after the patient leaves the OR
B. Only performed for masses
C. Accurately determines if the surgical margins are negative
D. Performed with magnification
22 When performing a stereotactic biopsy, what is stroke margin?
A. The distance from the image receptor to the tip of the needle postfire
B. The distance from the image receptor to the tip of the needle prefire
C. The distance of the lesion to the tip of the needle postfire
D. The distance of the lesion to the tip of the needle prefire
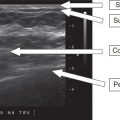
23 The image shown below is an ultrasound of the axilla in a patient with biopsy-proven breast cancer. A core needle biopsy was performed. Pathology shows benign reactive lymph node. The patient will receive which of the following procedures along with her lumpectomy?
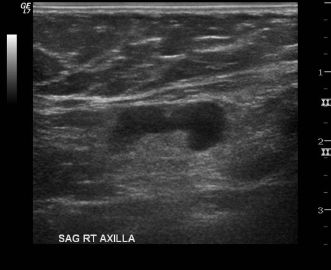
A. None
B. Rebiopsy is indicated prior to surgery.
C. Sentinel lymph node biopsy
D. Axillary dissection
24 Regarding stereotactic-guided breast biopsy, which of the following is correct?
A. A negative stroke margin is necessary to perform the biopsy.
B. Postprocedure mammogram is not necessary.
C. The most common complication is infection.
D. Specimen radiograph is performed to evaluate for adequate sampling.
E. The optimal needle approach is lateral.
25 Pathology for a core biopsy of this lesion imaged showed florid epithelial hyperplasia. What is the appropriate recommendation?
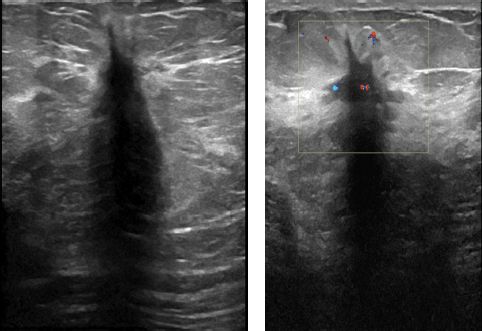
A. Surgical excisional biopsy
B. Breast-specific gamma imaging (BSGI)
C. Breast MRI
D. Follow-up diagnostic ultrasound in 6 months
26 Which of the following is a contraindication to whole-breast radiation therapy?
A. Axillary adenopathy
B. Collagen vascular disease
C. Residual microscopic disease
D. Younger women
27 The maximum dose of 1% lidocaine with epinephrine used for deep local anesthesia is
A. 7 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 500 mg
B. 7 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 1,000 mg
C. 10 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 500 mg
D. 10 mg/kg body weight, not to exceed 1,000 mg
28a A 47-year-old female with history of nipple discharge is referred from the breast surgeon for ductography. Which of the following is correct?
A. Ductography is indicated for single pore spontaneous nipple discharge.
B. Ductography is the procedure used to biopsy an intraductal mass.
C. Suspicious discharge includes spontaneous unilateral green or white discharge.
D. The standard dose of contrast used for ductography is 5 mL.
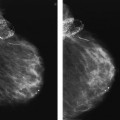
28b The following images are available from this patient’s ductogram. What is the next best step in patient management?
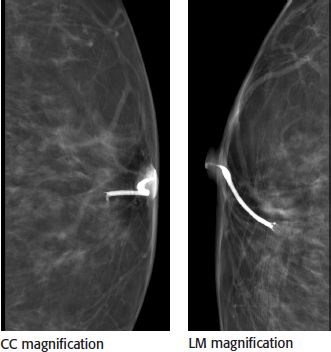
A. Stereotactic breast biopsy
B. Diagnostic breast MRI
C. Repeat ductogram due to artifact
D. Surgical breast biopsy
29 Which of the following statements concerning percutaneous biopsy is correct?
A. Correlation between pathology results and imaging studies does not have to be done for asymmetries.
B. Surgical excision is always recommended for atypical ductal hyperplasia and atypical lobular hyperplasia.
C. Pseudoaneurysms can occur in the breast after core biopsy.
D. Markers generally do not migrate after completion of stereotactic biopsy.
30 During galactography, how much contrast material is injected into the duct?
A. <0.3 mL
B. 0.3 to 1.0 mL
C. 2 to 4 mL
D. 3 to 6 mL
31 A stereotactic biopsy was performed on a 47-year-old patient. The pathology results are atypical ductal hyperplasia (ADH). What is the appropriate recommendation?
A. Surgical excision
B. MRI
C. 6-month follow-up
D. Repeat stereotactic biopsy
32 A 39-year-old female is scheduled for a contrast-enhanced breast MRI for high-risk screening evaluation. She undergoes laboratory testing for renal function due to her history of diabetes mellitus. Her laboratory results are creatinine of 1.8 mg/dL and a calculated GFR of 28 mL/min/1.73 m 2 . No prior laboratory data are available to review. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in the evaluation of this patient?
A. Consult with referring physician, and discuss risk–benefit ratio. If the examination is essential, use the lowest possible contrast dose as possible.
B. Proceed with the breast MRI without use of gadolinium-based contrast agent.
C. Proceed with the breast MRI using a standard dose of gadolinium-based contrast agent.
D. Cancel the breast MRI study.
33 Four days after a screening mammogram, a 40-year-old female discovers she is pregnant and estimates that the fetus is in its 3rd week of gestation. Which of the following is the most appropriate response regarding the amount of radiation the fetus received from the mammogram exam?
A. The fetus is unharmed because there was no radiation exposure.
B. The fetus is at potential risk of embryologic demise.
C. The fetus is at negligible risk for potential radiation-induced malformation of organs.
D. The child will have a 1% risk of developing severe mental retardation.
E. There is a high likelihood of a radiation-induced malformation of organs.
34 A 43-year-old female, with no known allergies or past medical condition, underwent an uneventful right breast stereotactic core needle biopsy in the morning. After needle biopsy, hemostasis was successfully achieved, and the patient was sent home. The patient returns to the radiology department complaining of right breast pain at the breast biopsy site. There is no oozing or unexpected bleeding or palpable lump at the biopsy site. Which of the following is the most appropriate initial management of the patient’s breast pain?
A. Give a prescription of Tylenol 3 (acetaminophen with codeine) for the patient to take as needed.
B. Give a prescription of Vicodin (acetaminophen with hydrocodone) for the patient to take as needed.
C. Advise the patient to take acetaminophen initially and then every 6 hours as needed, up to 4/d.
D. Advise the patient to take aspirin initially and then every 4 to 6 hours as needed, up to 3/d.
35 Which of the following situation can make stereotactic biopsy difficult, either requiring special repositioning of the patient or technically impossible?
A. Patient with breast thickness of 3 cm on the craniocaudal and breast thickness of 3.5 cm on mediolateral oblique view
B. A 2-mm cluster of pleomorphic microcalcifications in the central breast
C. Microcalcifications in the axillary tail region of the breast
D. A 3-cm segmental area of linear branching calcifications in the upper inner quadrant at a middle depth
36 A 31-year-old pregnant patient is discovered during her first trimester to have a breast cancer. The treatment for her breast malignancy is
A. None until after delivery
B. Immediate radiation therapy
C. Immediate chemotherapy
D. Immediate surgical resection
37 Which one of the following pathology results would most likely be considered discordant with the imaging findings of an irregular spiculated mass?
A. Postsurgical lumpectomy scar
B. Radial scar
C. Tubular carcinoma
D. Pseudoangiomatous stromal hyperplasia
ANSWERS AND EXPLANATIONS
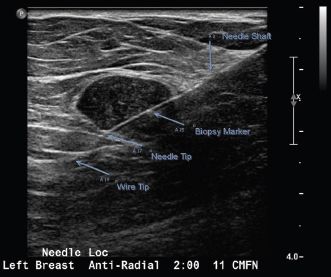
1 Answer D. The needle used in this case was a 5-cm rigid needle and J wire. The hook wire needle system is more commonly used. Both needle systems would look similar during the localization process. The difference between the two systems is with the hook wire system the needle is removed, leaving only the wire in the patient for surgery. The advantage is the patient does not have a needle in her breast as she awaits surgery. With the rigid needle and J wire system, both the needle and the wire remain in the patient, the advantage being the wire and needle are less likely to be accidentally pulled out of position within the target or completely pulled out of the breast while the patient awaits surgery. In this case, A is the needle shaft, B is the biopsy clip marker, C is the needle tip, and D is the wire tip. The needle is advanced completely through the lesion, and the wire is then advanced through the needle to ensure that the surgeon completely excises the entire lesion.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree