Bursitis
KEY FACTS
Terminology
Imaging
IMAGING
General Features
 Subacromial-subdeltoid bursa: Large bursa overlying rotator cuff tendons
Subacromial-subdeltoid bursa: Large bursa overlying rotator cuff tendons
 Olecranon bursa: Overlies olecranon process & distal end of triceps tendon
Olecranon bursa: Overlies olecranon process & distal end of triceps tendon
 Ischial tuberosity bursa: Between ischial tuberosity (hamstring tendon attachment) & gluteus maximus muscle
Ischial tuberosity bursa: Between ischial tuberosity (hamstring tendon attachment) & gluteus maximus muscle
 Iliopsoas bursa: Large bursa between iliopsoas tendon & anterior part of hip joint
Iliopsoas bursa: Large bursa between iliopsoas tendon & anterior part of hip joint
 Trochanteric bursa: Laterally overlies gluteus medius & minimus tendon insertion into greater trochanter femur
Trochanteric bursa: Laterally overlies gluteus medius & minimus tendon insertion into greater trochanter femur
 Subgluteus minimus bursa: Between gluteus minimus tendon & anterior facet greater trochanter
Subgluteus minimus bursa: Between gluteus minimus tendon & anterior facet greater trochanter
 Subgluteus medius bursa: Between gluteus medius tendon & posterosuperior facet greater trochanter
Subgluteus medius bursa: Between gluteus medius tendon & posterosuperior facet greater trochanter
 Semimembranous bursa: Posteromedial to semimembranous musculotendinous junction & tendon posteromedial aspect distal thigh
Semimembranous bursa: Posteromedial to semimembranous musculotendinous junction & tendon posteromedial aspect distal thigh
 Pes anserine bursa: Between sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus tendons, & posteromedial tibia
Pes anserine bursa: Between sartorius, gracilis, semitendinosus tendons, & posteromedial tibia
 Prepatellar bursa: Overlies inferior pole of patella & proximal patellar tendon
Prepatellar bursa: Overlies inferior pole of patella & proximal patellar tendon
 Infrapatellar bursa: Overlies mid-to-distal aspect of patellar tendon
Infrapatellar bursa: Overlies mid-to-distal aspect of patellar tendon
 Retrocalcaneal bursa: Between calcaneus, Achilles tendon, & Kager fat pad
Retrocalcaneal bursa: Between calcaneus, Achilles tendon, & Kager fat pad
 Superficial calcaneal bursitis: Overlies distal aspect of Achilles tendon
Superficial calcaneal bursitis: Overlies distal aspect of Achilles tendon
Ultrasonographic Findings
 Majority of bursae not visible on US unless distended with fluid or proliferative synovial tissue
Majority of bursae not visible on US unless distended with fluid or proliferative synovial tissue
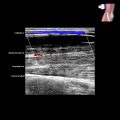
 Distended hypoechoic bursa
Distended hypoechoic bursa
 Acute bursitis: Thin-walled bursa distended with hypoechoic fluid, peribursal hyperemia
Acute bursitis: Thin-walled bursa distended with hypoechoic fluid, peribursal hyperemia
 Chronic cases: Greater thickening of bursal wall, more mature synovial proliferation, more echogenic content, & increased likelihood of intrabursal hyperemia
Chronic cases: Greater thickening of bursal wall, more mature synovial proliferation, more echogenic content, & increased likelihood of intrabursal hyperemia







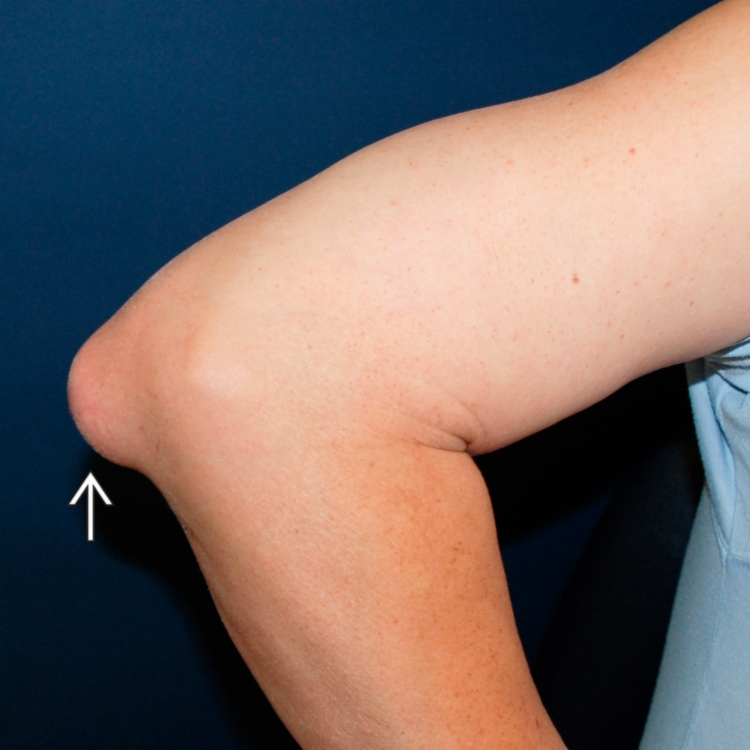
 that has been present for years but recently increased in pain and size.
that has been present for years but recently increased in pain and size.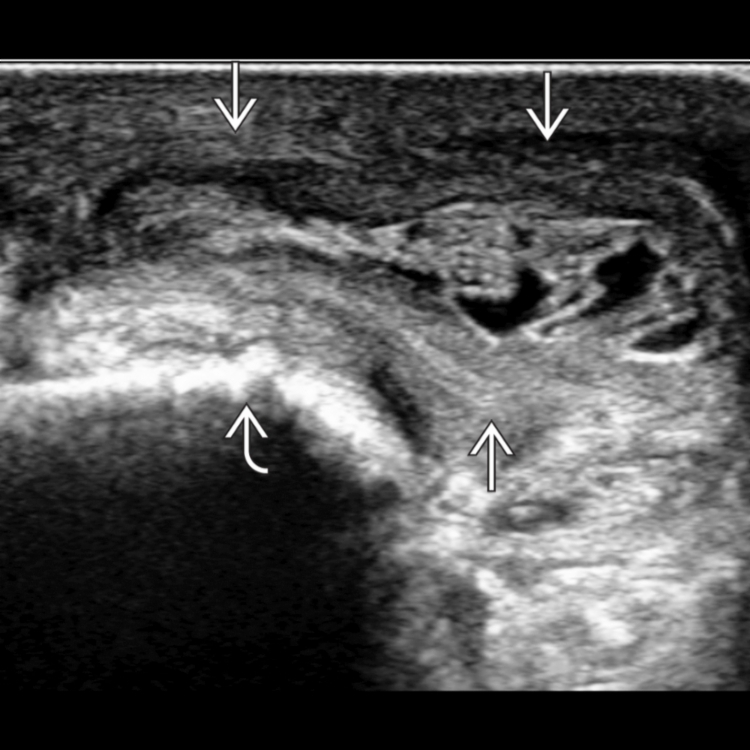
 . The bursa is distended by fluid and synovial proliferation and overlies the olecranon process
. The bursa is distended by fluid and synovial proliferation and overlies the olecranon process 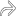 . Olecranon bursae frequently have a thickened wall, internal debris, and septa. A noninflamed olecranon bursa is not visible on US.
. Olecranon bursae frequently have a thickened wall, internal debris, and septa. A noninflamed olecranon bursa is not visible on US.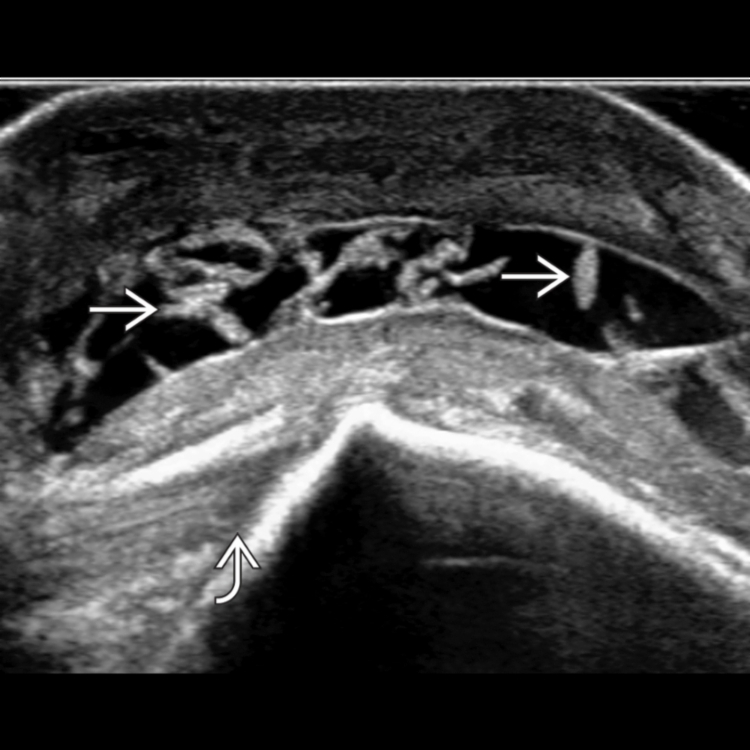
 , giving the bursa a multiloculated appearance. The normal triceps tendon insertion
, giving the bursa a multiloculated appearance. The normal triceps tendon insertion 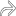 into the olecranon process is shown.
into the olecranon process is shown.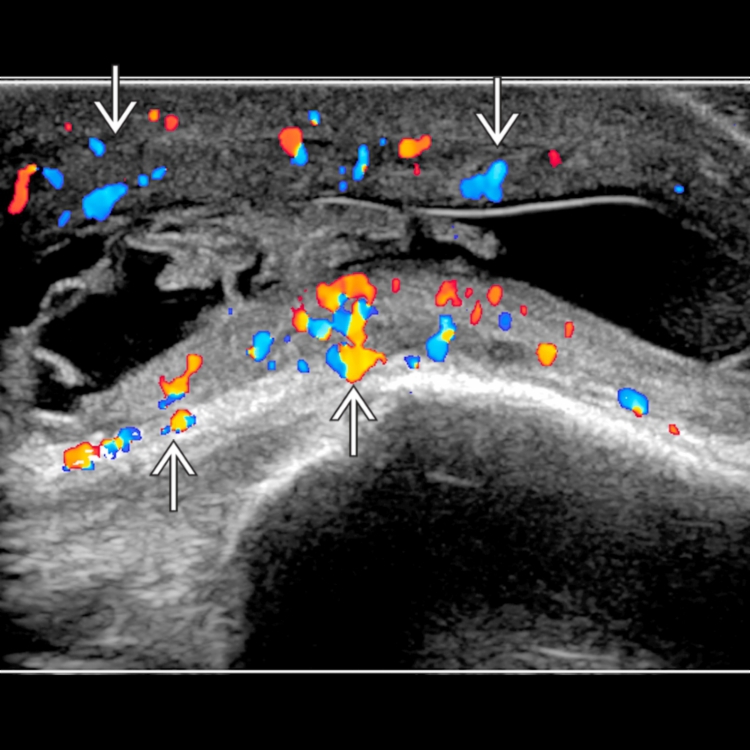
 and peribursal tissues. The internal content and septations show no hyperemia.
and peribursal tissues. The internal content and septations show no hyperemia.