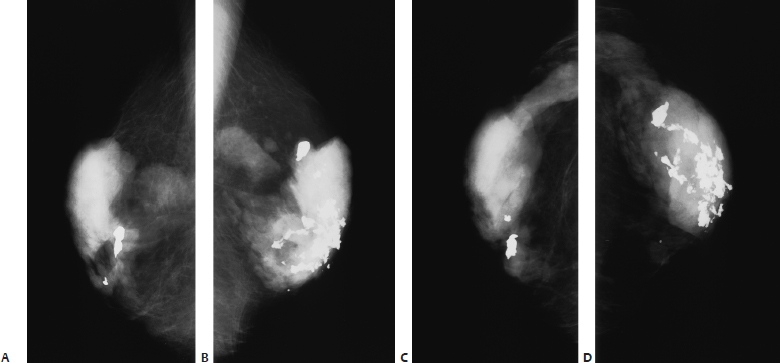
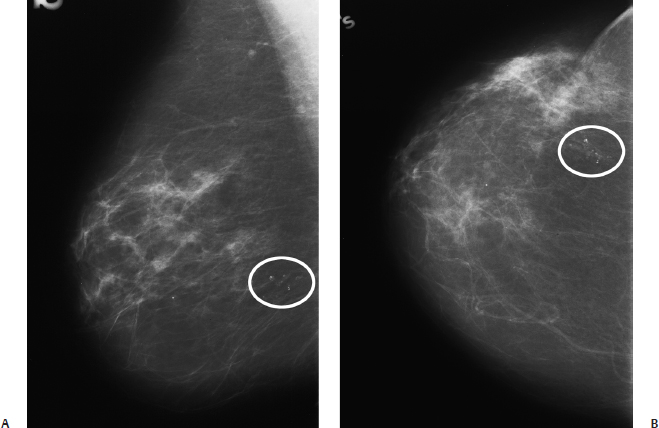
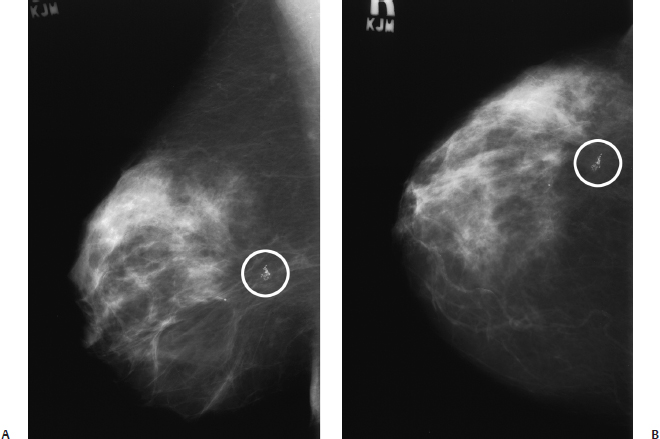
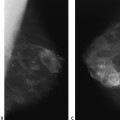
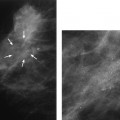
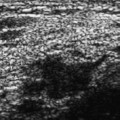
15 Calcifications: Dystrophic An 84-year-old woman presents for screening mammogram. • Scars in both breasts from previous reduction mammoplasties Calcifications (Fig. 15.1) • Type: dystrophic • Distribution: diffuse/scattered Fig. 15.1 In both breasts there are large, coarse, dystrophic calcifications that have resulted from this patient’s bilateral reduction mammoplasties. (A) Right MLO mammogram. (B) Left MLO mammogram. (C) Right CC mammogram. (D) Left CC mammogram. • Fat necrosis • BI-RADS assessment category 2, benign finding • Fat necrosis may be associated with round (oil cyst), eggshell/rim, or large, irregular calcifications. This case is an example of the last type of calcification. Sickles EA. Breast calcifications: mammographic evaluation. Radiology 1986;160:289–293 A 79-year-old woman presents with right breast calcifications. • Normal exam Calcifications (Figs. 15.2 and 15.3) • Type: dystrophic • Distribution: grouped/clustered Fig. 15.2 In the right outer breast, there is a cluster of calcifications (circle) that was biopsied after this examination. (A) Right MLO mammogram. (B) Right CC mammogram. Fig. 15.3 Five years after the mammographic examination shown in Fig. 15.2, the calcifications (circle) have become large and coarse. (A) Right MLO mammogram. (B) Right CC mammogram. • Scar
Case 15.1: Fat Necrosis
Case History
Physical Examination
Mammogram
Pathology
Management
Pearls and Pitfalls
Suggested Reading
Case 15.2: Fat Necrosis
Case History
Physical Examination
Mammogram
Pathology
Management
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree