26 Cardiac failure and pulmonary oedema
Background
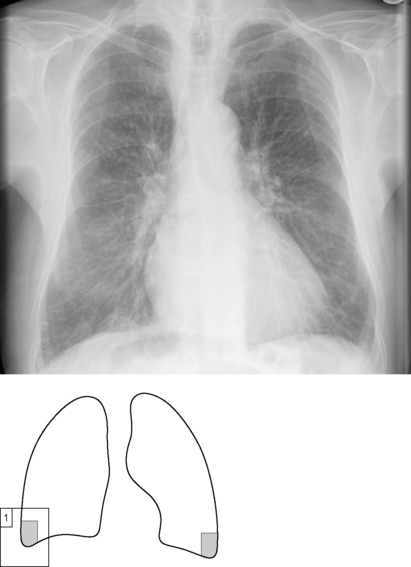
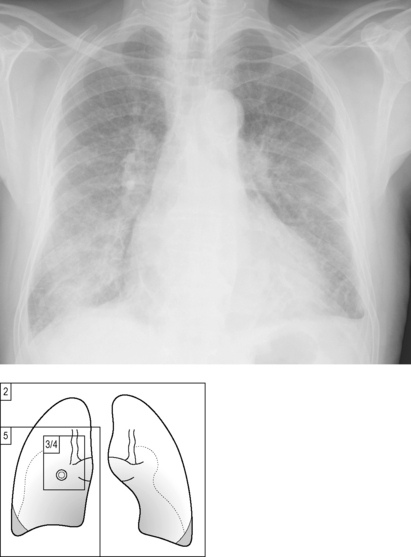
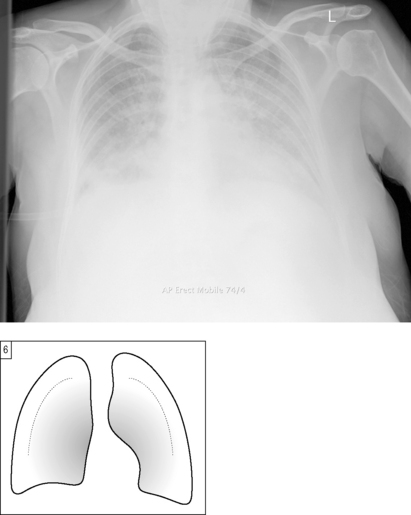
The commonest causes of pulmonary oedema encountered by the on-call doctor are cardiac failure and iatrogenic fluid overload. The latter should be clear within its clinical context. Cardiogenic pulmonary oedema coexists with cardiac enlargement. See the section on PA versus AP projection, Chapter 6, page 37.
Clinical features
Symptoms
Symptoms include dyspnoea, orthopnoea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnoea and peripheral oedema.
Differential diagnosis
Other types of fluid in the alveoli can cause unilateral or bilateral but often asymmetric airspace shadowing, for example pus in pneumonia (Chapter 8) blood in contusion and bronchioloalveolar carcinoma.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree