Cavity Spinwand
Donald V. La Barge, III, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Cavity creation via plasma field ablation of vertebral body neoplasms prior to cement injection
Pre-Procedure
Indication
Spinal tumor ± pathological fracture
Pre-procedure imaging
Cortical breakthrough/epidural extension of tumor
Assessment of relevant anatomy/satisfactory pedicle integrity for access
Procedure
Gain bipedicular vertebral access
Perform percutaneous vertebral biopsy
Perform percutaneous tumor ablation/cavity creation (Coblation)
Follow manufacturer’s instructions
Start low with current, and increase as tolerated
Carefully fill cavity with bone cement under continuous fluoroscopy to ensure safe injection
Must check PA and lateral views intermittently to avoid venous/extraosseous cement injection
Always remain aware of extravasation via expected locations of cortical breakthrough or epidural tumor extension
Post-Procedure
Improved pain score
87% reported improvement in pain at 2-4 weeks post procedure
Less recovery time and cost compared with open surgery
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Coblation (ArthroCare; Sunnyvale, California), tumor debulking void-enhanced vertebroplasty
Definitions
Cavity creation via plasma field ablation of vertebral body neoplasms prior to cement injection/vertebral augmentation
PRE-PROCEDURE
Indications
Primary or metastatic spinal tumor ± pathological fracture
Getting Started
Things to check
Pre-procedure imaging
Cortical breakthrough/epidural extension of tumor
Assessment of relevant anatomy/satisfactory pedicle integrity for access
Pre-procedure pain scale
Informed consent
Medications
Antibiotics immediately before procedure (1 g of cefazolin sodium, if not contraindicated)
Equipment list
Radiopaque marker
Standard prep and drape materials
Local anesthetic
22-gauge spinal needle if needed to anesthetize pedicle
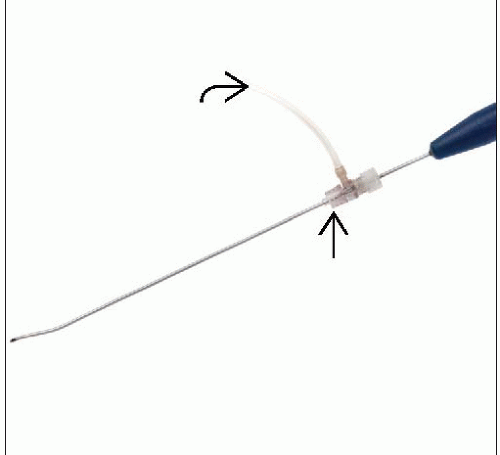
Vertebral access needle adequate to permit passage of Cavity SpineWand (ArthroCare; Sunnyvale, California) (8- or 11-gauge)
Bone biopsy needle
Cavity SpineWand and associated equipment to include saline flush
Bone cement and injector
PROCEDURE
Patient Position/Location
Best procedure approach
Prone
Equipment Preparation
Ensure proper functioning of Cavity SpineWand power generating system
Ipsilateral oblique will show ovoid pedicle; stop oblique where maximal pedicle size is seen (“down the barrel” view)
Biplane fluoroscopy is ideal, enabling 1 tube to provide direct lateral fluoroscopy at all times
Procedure Steps
“Time out” with all team members present
Proper patient, procedure, and level(s) to be intervened upon
Ensure correct spinal level(s), and mark skin
Initiate conscious sedation
Provide local anesthetic
Use of 22-gauge spinal needle is advantageous in many cases to anesthetize pedicle cortex
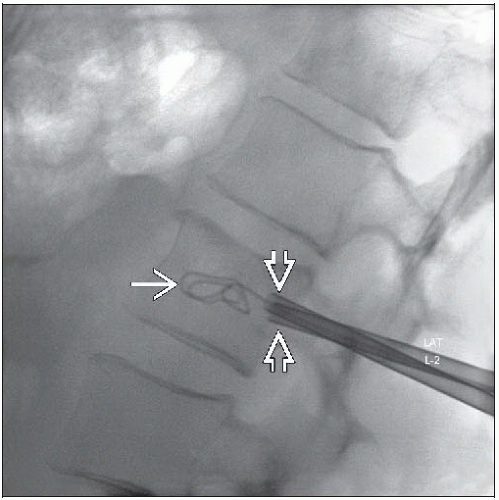
Guide access needle to pedicle cortex (using “down the barrel” ipsilateral oblique view)
Check lateral fluoroscopy prior to anchoring needle to ensure accurate trajectory
Ensure that needle trajectory will not violate medial pedicle cortex on AP/oblique view
Anchor access needle in pedicle cortex, and recheck trajectory
Under intermittent AP and lateral fluoroscopy, advance needle to vertebral body to permit accurate biopsy and Cavity SpineWand placement within tumor
Perform percutaneous vertebral biopsy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree