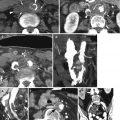
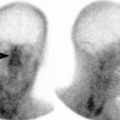
Celiac Plexus Block
Lubdha M. Shah, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Palliative procedure in cases of severe upper abdominal pain caused by pancreatitis or advanced cancers of the upper abdominal viscera, especially pancreatic cancer
Blocks transmission of pain by treating CP with a neurolytic agent, such as alcohol
Can be guided by bony landmarks, fluoroscopy, ultrasound, CT, MR, or endoscopic ultrasound
Abdominal visceral pain is mediated through nerve fibers that travel from viscera → celiac ganglia → splanchnic nerves
Procedure
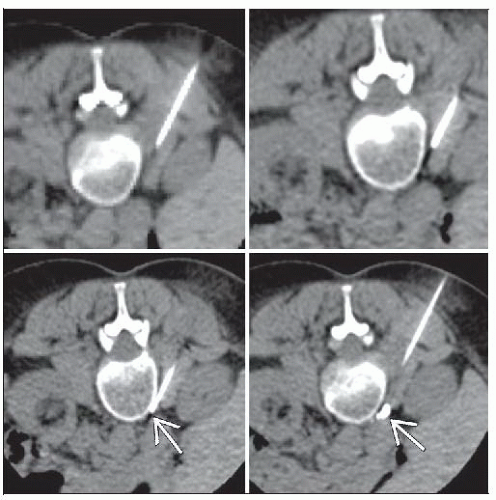
Posterior (antero- or retrocrural) or anterior approach
CT guides accurate positioning of needle(s) in vicinity of CP while avoiding penetration or injection into spinal cord, major vascular structures, liver, kidneys, and bowel
Post-Procedure
Success of CPB is dependent on effective distribution of neurolytic agent throughout entire CP
In some cases, regional tumor infiltration or scar tissue and fibrosis can limit access to celiac plexus & prevent effective delivery of neurolytic agent
Outcomes
Complications
Paraplegia
Vascular injury
Hypotension or diarrhea due to loss of sympathetic tone and splanchnic vasodilation/unopposed parasympathetic influence
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Celiac plexus block (CPB)
Synonyms
Splanchnic plexus block/neurolysis
Periaortic sympathetic plexus block/neurolysis
Definitions
Palliative procedure in cases of severe upper abdominal pain caused by pancreatitis or advanced cancers of the upper abdominal viscera, especially pancreatic cancer
Blocks transmission of pain by treating celiac plexus (CP) with a neurolytic agent, such as alcohol
Can be guided by bony landmarks, fluoroscopy, ultrasound, CT, MR, or endoscopic ultrasound
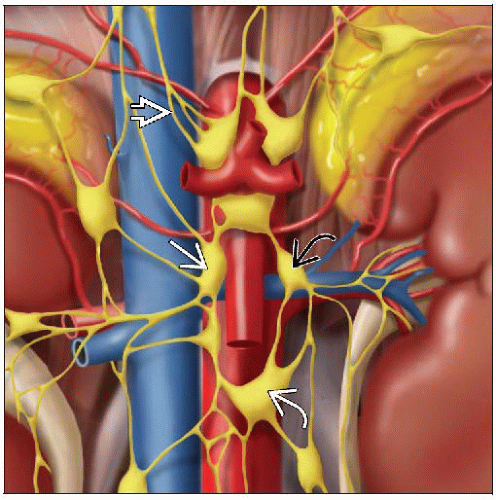
Anatomy
Abdominal visceral pain is mediated through nerve fibers that travel from the viscera → celiac ganglia → splanchnic nerves
CP: Autonomic efferents (supply upper abdominal viscera) & visceral afferents (supply abdominal viscera from distal esophagus to transverse colon)
Block at ganglion level: Afferents innervating abdominal & pelvic organs travel in/along sympathetic nerves, trunks, ganglia, & rami
Splanchnic nerve blocks will affect only sympathetic efferent and afferent pathways
CP consists of 1 to 5 pairs of ganglia ranging in size from 0.5-4.5 cm: The celiac, the aortic-renal, and the superior mesenteric
Variable location of CP with regard to bony landmarks; more reliably found close to ostia of celiac artery
˜ 0.6 cm caudad to celiac artery on right and 0.9 cm caudad to celiac artery on left
Retro- and anterocrural space is well-defined anatomic compartment that restricts spread of neurolytic agent
3 components: Aorta, crura of diaphragm, vertebral body
PRE-PROCEDURE
Indications
Severe chronic abdominal pain due to advanced cancers of the upper abdominal viscera, especially pancreatic cancer
Blocking transmission of pain with a neurolytic agent, such as alcohol, can decrease the need for opiates and limit opioid side effects, especially constipation
Alcohol destroys nerves by dissolving their fatty sheaths but has little effect on other nearby structures such as the muscular wall of the aorta
Contraindications
Uncooperative patient
Coagulopathies
Getting Started
Things to check
Allergies, coagulation labs
History of prior abdominal surgeries that may affect procedural approach and efficacy of diffusion of neurolytic agent
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree