KEY FACTS
Imaging
- •
Soft tissue mass in cervix: Hypoechoic or isoechoic ± necrosis
- •
Hydro- or hematometra from cervical obstruction
- •
Mass extending into upper vagina
- •
MR is best modality for local staging and planning of radiation therapy
- ○
Tumor: Intermediate- to high-signal mass replacing dark cervical stroma on T2-weighted sequences
- ○
Accuracy superior to FIGO staging for size, parametrial extension, lymph nodes
- ○
Parametrial invasion: Accuracy: 88-97%, specificity: 93%, negative predictive value: 94-100%
- ○
- •
PET/CT best modality for overall staging: Nodal disease, liver, bone, and lung metastases
- •
Revised FIGO staging uses information from CT or MR; cystoscopy and sigmoidoscopy not mandatory
- •
Invasion of posterior bladder wall, anterior rectal wall, ureters
- ○
Hydronephrosis implies stage IIIB disease
- ○
- •
Enlarged lymph nodes
- •
Abundant internal color flow on color Doppler
- •
3D US may be used to assess tumor volume before/after therapy
- •
Ultrasound may be used to guide placement of radiotherapy instruments
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Cervical fibroid
- •
Cervical polyp
- •
Endometrial cancer invading cervix
- •
Adenoma malignum/minimal deviation adenocarcinoma
- •
Rarer cervical tumors: Lymphoma, neuroendocrine/small cell carcinoma
Pathology
- •
~ 80-90% are squamous carcinoma
- •
Arise at squamocolumnar junction from precursor lesions
- ○
Cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grades I-III
- ○
- •
Stage I: Confined to cervix
- •
Stage II: Beyond uterus but not to pelvic sidewall or lower 1/3 of vagina
- •
Stage III
- ○
IIIA: Lower 1/3 of vagina
- ○
IIIB: Pelvic side wall (within 3 mm of obturator internus, levator ani or pyriformis muscles, or iliac vessels) or hydronephrosis/nonfunctioning kidney
- ○
- •
Stage IV: Bladder/rectal involvement or distant metastases (lung, liver, bones)
- •
Presence of pelvic or paraaortic lymphadenopathy alters prognosis but not FIGO stage
Clinical Issues
- •
Abnormal bleeding, pain, or discharge
- •
Detected by screening cytology from Pap smear
- ○
± testing for high-risk HPV
- ○
- •
3rd most common gynecologic malignancy in USA and most common gynecologic malignancy worldwide
- •
Risk factors: HPV infection most important, early-onset sexual activity, multiple partners, smoking, immunosuppression, HIV infection
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for disruption of normal cervical morphology
- ○
And for abnormal color flow
- ○
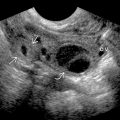
 , proven to be squamous cell carcinoma. The body of the uterus
, proven to be squamous cell carcinoma. The body of the uterus  was unremarkable.
was unremarkable.
 of the cervical carcinoma.
of the cervical carcinoma.
 . Local staging cannot be determined. There is no hematometra
. Local staging cannot be determined. There is no hematometra  .
.
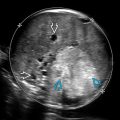
 , extending onto the right parametrium
, extending onto the right parametrium  and growing along ligaments
and growing along ligaments  . Bilateral ovaries
. Bilateral ovaries  are not usually involved.
are not usually involved.