Cholangiocarcinoma
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Amir A. Borhani, MD
Key Facts
Imaging
Klatskin tumor: Small hilar mass obstructing bile ducts on CT or ERCP
Cholangiography (PTC/ERCP)
Important to determine extent of intra- and extrahepatic duct involvement
Extension up right or left duct often precludes surgical resection
CECT
Portal phase: Minimal enhancement of irregularly thickened bile duct wall and distal ductal dilatation
Delayed phase: Persistent enhancing tumor (due to fibrous stroma)
MR
Superior to CT for detection of small hilar tumors, intrahepatic & periductal tumor infiltration
Shows location of obstruction and IHBD dilatation
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
Chronic pancreatitis
Choledocholithiasis
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Autoimmune pancreatitis/cholangitis
Inflammatory hepatic pseudotumor
Pathology
Tumor types
Exophytic intrahepatic masses (nodular type)
Scirrhous infiltrating neoplasms (sclerosing type): Cause strictures
Polypoid neoplasms of ductal wall (papillary type): Bulge into bile duct lumen
Risk factors
PSC
Fibropolycystic liver disease (choledochal cysts)
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Cholangiocarcinoma (CCa)
Synonyms
Cholangiocellular or bile duct adenocarcinoma
Definitions
Malignancy arising from intrahepatic bile duct (IHBD) or extrahepatic bile duct epithelium
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Klatskin tumor: Small hilar mass obstructing bile ducts on CT or ERCP
Location
Distribution in different segments of biliary tree
Distal common bile duct (CBD) (30-50%)
Common hepatic duct (14-37%)
Proximal CBD (15-30%)
Confluence of hepatic ducts (Klatskin tumor) (10-26%)
Isolated left or right hepatic duct (8-13%)
Cystic duct (6%)
Classified based on anatomy and radiography
Peripheral (10%)
Intrahepatic; proximal to secondary biliary radicles
Perihilar (50%)
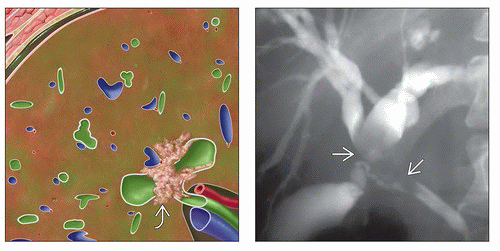
Klatskin tumor: Hilar tumor involving the confluence of hepatic ducts
Distal (40%)
Extrahepatic; distal CBD
May arise as short stricture or small polypoid mass
Size
Peripheral cholangiocarcinoma (5-20 cm)
Perihilar and extrahepatic types much smaller
Morphology
Infiltrative (sclerosing)
Exophytic (nodular)
Papillary
Radiographic Findings
Cholangiography (PTC/ERCP)
Papillary intraductal tumor mass (2-5 mm in diameter)
Infiltrating type: Frequently long, rarely short, concentric focal stricture
Ductal wall irregularities, prestenotic diffuse/focal biliary dilatation
Hilar strictures (due to Klatskin tumor): Proximal bile duct dilatation
Important to determine extent of intra- and extrahepatic duct involvement
Extension up right or left duct often precludes surgical resection
CT Findings
NECT
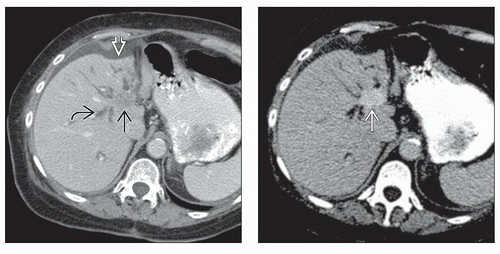
Intrahepatic
Peripheral hypodense solitary or satellite lesions and IHBD dilatation
Capsular retraction is often seen
Central (hilar) hypodense mass at confluence and IHBD dilatation
Extrahepatic: Common duct
Small mass (hard to detect on CT or MR)
Large growth (seen as hypodense mass) and IHBD dilatation
CECT
Arterial phase
Early rim enhancement with progressive, central, patchy enhancement
Portal phase
Minimal enhancement of irregularly thickened bile duct wall
Dilated IHBD
Invasion of portal vein often seen with intrahepatic type
Enlarged portal lymph nodes may be seen
Delayed phase
Persistent enhancing tumor (due to fibrous stroma)
MR Findings
T1WI
Iso- or hypointense
T1WI FS
Shows tumor of intrapancreatic portion of CBD as low signal intensity against high signal intensity of pancreatic head
T2WI
Hyperintense periphery (viable) and central hypointensity (fibrosis)
T1WI C+
Superior to CT in detecting small hilar tumors, intrahepatic and periductal tumor infiltration
MRCP
Reveals site and extension of tumor growth
Shows location of obstruction and IHBD dilatation
Ultrasonographic Findings
Grayscale ultrasound
Mixed echoic, homo-/heterogeneous mass and dilated IHBD
Dilated intra- and extrahepatic bile ducts if lesion is in CBD
Endoscopic ultrasound (EUS)
Reported higher sensitivity than CT, US, and cholangiography
Angiographic Findings
Conventional
Avascular, hypo-/hypervascular
Poor or absent tumor stain
Hepatic artery and portal vein
Displacement, encasement, or occlusion
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree