KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Choroid plexus cysts (CPC) are unilocular cysts usually located in the posterior thick portion of choroid plexus
Imaging
- •
CPC are most often incidental isolated findings
- ○
Almost all resolve by 32 weeks
- ○
Might be large, multiple, or bilateral
- ○
Not associated with aneuploidy in low-risk patients
- ○
- •
CPC may be seen in trisomy 18 (T18)
- ○
Anomalies and growth restriction almost always present
- –
Cardiac and extremity anomalies common
- –
- ○
CPC > 10 mm associated with mild ↑ risk for T18
- ○
Multiple and bilateral CPC do not ↑ risk for T18
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Intraventricular hemorrhage
- ○
Blood clot adherent to choroid might mimic CPC
- ○
Echogenic ventricular wall, ventriculomegaly
- ○
- •
Choroid plexus papilloma (rare)
- ○
Vascular mass, ventriculomegaly
- ○
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Is patient low risk for aneuploidy? Has she had testing?
- ○
Cell-free DNA test results (best)
- ○
Maternal serum biochemistry results
- ○
Consider genetic counseling if patient has had no testing
- ○
- •
Follow-up to show CPC resolution is not necessary
Scanning Tips
- •
Do detailed scan of fetus when CPC is seen
- ○
Extra cardiac views
- –
Outflow and inflow tract views
- –
- ○
Extra extremity views
- –
Open hands, normal feet
- –
- ○
- •
Scan in multiple planes to show cyst located in choroid
- ○
Large cysts may be mistaken for ventriculomegaly
- ○
Normal fluid-filled atria may mimic CPC
- ○
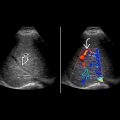
 occurring in the posterior, thick portion of the choroid plexus (glomus of choroid) is shown. The choroid plexus produces cerebrospinal fluid, and CPCs are considered “entrapment cysts”.
occurring in the posterior, thick portion of the choroid plexus (glomus of choroid) is shown. The choroid plexus produces cerebrospinal fluid, and CPCs are considered “entrapment cysts”.