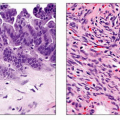
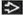Chronic Pancreatitis
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Irreversible inflammatory damage to pancreas, usually evident on imaging or functional testing
Imaging
Approximately 90% of cases of calcific pancreatitis are due to alcoholism
Other 10% = mostly hereditary pancreatitis
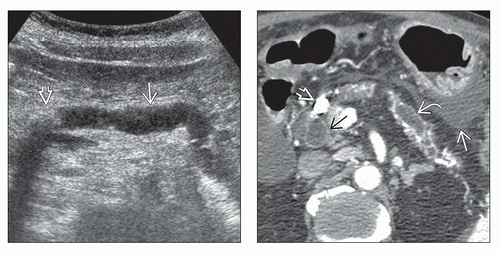
Atrophy of gland, dilated main pancreatic duct (MPD), intraductal calculi
Fibroinflammatory mass: Common in pancreatic head
May have “double duct” sign (stricture of distal CBD and pancreatic duct)
Not pathognomonic of pancreatic carcinoma
Long, smooth taper of CBD (not abrupt, as with carcinoma)
MRCP: Good depiction of parenchymal and ductal lesions
Splenic vein thrombosis, splenomegaly, varices
May progress to thrombosis of portal vein
Pseudoaneurysm of gastroduodenal or other arteries
Detected by US, CTA, or MRA
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pancreatic ductal carcinoma
Pancreatic IPMN
Senescent change
Pathology
Gallstones, hyperlipidemia, trauma; drugs often cause acute and recurrent, but rarely chronic, pancreatitis
Genetic predisposition toward pancreatitis from alcohol
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Irreversible inflammatory damage to pancreas, usually evident on imaging or functional testing
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Atrophy of gland, dilated main pancreatic duct (MPD), intraductal calculi
Size
Pancreas usually decreased in size (atrophy)
Morphology
Inflammatory disease of pancreas characterized by irreversible damage to morphology and function
Pancreatic calcification
Almost diagnostic of chronic pancreatitis
Approximately 90% of calcific pancreatitides are caused by alcoholism
Other 10% = mostly hereditary pancreatitis
40-60% of patients with alcoholic pancreatitis
Other features
75% of cases in USA are due to alcoholism
Developing countries: Malnutrition and alcoholism
Radiographic Findings
Radiography
Plain abdomen radiograph
Pancreatic calcification
Small, irregular calcifications (local or diffuse)
Barium (UGI series)
Changes seen in 2nd part of duodenum
Varying degrees of atony
Thickened, irregular mucosal folds; luminal narrowing
Dilatation of proximal duodenum ± stomach
Enlarged papilla of Vater
ERCP
Dilated and beaded main and side branches of pancreatic duct
MPD filling defects: Intraductal calculi
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree