CHAPTER 11 Common Inherited and Metabolic Disorders
Metabolic and inherited disorders are routinely encountered in pediatric radiology, where they often dominate the disease spectrum, and thus are more easily brought to mind when formulating differential diagnoses. In adult radiological practice, by contrast, most disease processes are acquired and a few general disease categories predominate, namely, neoplastic, traumatic, infectious, and inflammatory diseases. With few exceptions, no isolated finding on an abdominal imaging examination is pathognomonic for an inherited or metabolic disorder. However, an atypical distribution or multiplicity of a common lesion, or the coexistence of particular imaging findings should invite consideration of this disease category. As our knowledge of inherited diseases increases, it is likely that the list of inherited disorders and syndromes will continue to grow.
The goal of this chapter is to provide a practical, organ-system–based approach to commonly encountered inherited and metabolic diseases (Tables 11-1 and 11-2). Because of the vast number of potential hereditary syndromes, the focus has been kept on describing some of the more commonly encountered or discussed syndromes with typical abdominal imaging manifestations in adults. A detailed description of the germline mutations and other specific genetic features for each of the inherited conditions is beyond the scope of this chapter, but the Suggested Readings at the end of this chapter list several excellent references for further information. To avoid redundancy, we do not discuss the imaging appearance of the specific abnormalities that comprise each entity in any detail. Instead, the imaging appearances of the various cysts, tumors, and other abnormalities that may comprise a particular syndrome are discussed in detail in the organ-specific chapters in Section III of this textbook.
Table 11-1 Alphabetical List of Select Inherited and Metabolic Disorders with Imaging Manifestations in the Adult
| Disorder | Abdominal Region | Extraabdominal Regions |
|---|---|---|
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) | ||
| Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) | ||
| Caroli disease | ||
| Congenital hepatic fibrosis | ||
| Cowden disease | ||
| Cystic fibrosis (CF) | ||
| Diabetes mellitus | ||
| Familial adenomatous polyposis syndrome (FAP) | ||
| Gardner syndrome | ||
| Gaucher disease (β-glucocerebrosidase deficiency) type I | ||
| Glycogen storage disease type I | Osteoporosis | |
| Glycogen storage disease type III | Cardiomegaly | |
| Hereditary hemochromatosis | ||
| Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia (HHT) | ||
| Lynch syndrome (hereditary nonpolyposis colorectal cancer syndrome [HNPCC]) | CNS tumors | |
| Multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN) type 1 | ||
| MEN type 2 | ||
| Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1) | ||
| Peutz–Jeghers syndrome | Extraabdominal malignant tumors (e.g., lung, breast, esophagus) | |
| Sickle cell disease* | ||
| Tuberous sclerosis complex | ||
| Turcot syndrome | Malignant CNS tumors | |
| von Hippel–Lindau disease | Retinal and CNS hemangioblastomas |
Lists do not represent diagnostic criteria; they represent findings that may be present on imaging studies and findings for which patients are at increased risk. Not all findings listed will be present in all patients.
* Manifestations depend on homozygous or heterozygous state.
Table 11-2 Abdominal Imaging Combinations That Suggest Inherited Disorder
| Combination of Findings Present | Disorders to Consider |
|---|---|
| Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease | |
| von Hippel–Lindau disease | |
| Tuberous sclerosis complex | |
| Congenital hepatic fibrosis | |
| Gardner syndrome | |
| Sickle cell disease | |
| Cystic fibrosis | |
| Gaucher disease | |
| Neurofibromatosis type 1 | |
| Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia |
HEPATOBILIARY ABNORMALITIES
Diffuse Liver Disease
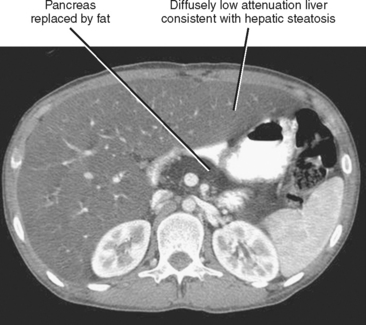
Steatosis
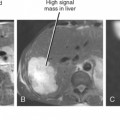
The excess deposition of fat within hepatocytes can result from a large number of acquired factors and inherited metabolic derangements. Hepatic steatosis manifests on imaging studies as increased liver echogenicity (ultrasound) or decreased liver density (computed tomography [CT]). With MRI, the steatotic liver appears as higher than normal signal intensity on non–fat-suppressed T1-weighted images. On in- and opposed-phase gradient-echo images (chemical shift imaging), the steatotic liver loses signal on opposed-phase images relative to in-phase images. Some better known metabolic and inherited causes of hepatic steatosis are listed in Box 11-1.