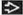Complications of Neck Radiation Therapy
Christine M. Glastonbury, MBBS
Key Facts
Terminology
Uncommon, unwanted side effects from radiation therapy (XRT) seen in small proportion of patients
Imaging
Potentially involves any radiated neck tissue
Excessive inflammation, tissue necrosis, or tumor induction
CT or MR may be complementary for detection and characterization of abnormality
CECT typically first-order examination; evaluates soft tissues and bones
Mucosal ulceration and fistulae, myositis, osteoradionecrosis, chondronecrosis
MR best for nervous system complications
Cerebral radionecrosis, myelopathy, brachial plexitis, cranial neuropathy
PET may be misleading; focal FDG uptake common
Top Differential Diagnoses
Recurrent tumor
Skull base or mandible-maxilla osteomyelitis
Pathology
XRT results in obstructive arteriopathy
Tissues less able to withstand additional stress
Infection, tumor recurrence, or biopsy may precipitate necrosis
Clinical Issues
Uncommon; ˜ 1% of patients receiving neck XRT
Most complications occur ≤ 2 years after XRT
May occur up to 5-8 years post XRT
Treatment is largely conservative
Diagnostic Checklist
Key differential is always residual/recurrent tumor
Look for solid enhancing mass
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Uncommon, unwanted side effects from radiation therapy (XRT) seen in small proportion of patients
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
No. 1 diagnostic feature, as this potentially involves any radiated tissue in neck and may be marked inflammation, tissue necrosis, or tumor induction
Tissue necrosis: Soft tissue, muscle, cartilage, bone, brain parenchyma
Marked inflammation: Brachial plexus, cervical cord, cranial nerves, muscles
Radiation arteriopathy: Carotid vessels
Tumor induction: Radiation-induced neoplasm
Imaging Recommendations
Best imaging tool
CT or MR may be used for detection and characterization of abnormality
Modalities often complementary, particularly for bone lesions
Solid enhancing mass raises concern for tumor recurrence
MR best for evaluation of nervous system complications
PET/CT often misleading in neck
Focal FDG uptake may be seen with necrosis
Probably due to accompanying infection/inflammatory response
Must interpret with CECT or MR
CT Findings
CECT
Findings vary with site of complication
Mucosa & submucosa: Necrosis and ulceration → fibrosis
Early: Mucosal ulceration common; if solid enhancement, concern for tumor
Rarely, severe edema results in airway narrowing
Deep ulceration may lead to fistula
Late: May result in fibrotic, stenotic pharynx
Smooth, minimally enhancing wall
Absence of enhancing mass favors necrosis and ulceration over residual/recurrent tumor
Muscles: Myositis to fibrosis
Early: Marked swelling and decrease in density
Late: Marked volume loss of muscles
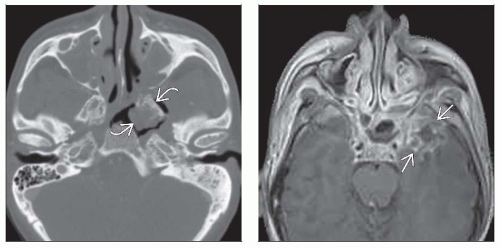
Cartilage: Chondronecrosis
Fragmentation of cartilage associated with soft tissue swelling
± gas bubbles adjacent to cartilage
Bones: Osteoradionecrosis (ORN)
Bony cortical disruption, loss of trabeculae
± sequestrum, fragmentation, fracture, gas
May have soft tissue thickening, fistula
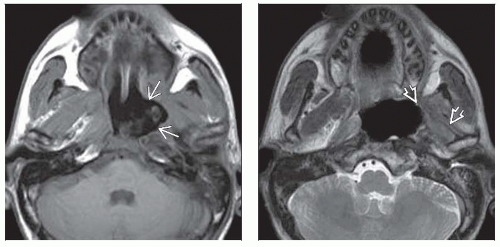
Brain parenchyma: Cerebral radionecrosis
White matter edema with mass effect
Enhancement may be difficult to detect on CECT
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree