14 Computed tomography (CT) scanning
Definition of computed tomography scanning
| Is the process of producing a cross-sectional image of the body by using a collimated beam of radiation that rotates round the patient. Some of the radiation is absorbed and scattered by the body and some is transmitted through the patient and is collected by a number of detectors which are linked to photomultipliers. A signal is then sent to a computer which calculates the amount of radiation absorbed by the patient and reconstructs an image which can then be viewed on a television monitor |
| Dynamic CT | When a number of scans are performed in rapid succession, e.g. to demonstrate blood flow |
| Enhanced CT | The use of a contrast agent to improve the appearance of vessels or organs that are similar in density to the surrounding tissues |
| Field of View | The part of the scanned plane which may be included in the final image |
| Helical | Spiral |
| Image Acquisition | The collection of data in order to produce an image |
| Image Format | The process of storing an image, on computer disk, magnetic tape, film or on the World Wide Web |
| Image Manipulation | To digitally change the appearance of the acquired image in order to improve it |
| Image Reconstruction | The process of generating an image from raw data or a set of unprocessed measurements |
| Isotropic | Having the same properties in all directions, e.g. density |
| Matrix | The columns and rows that form a digital image |
| Mean Window Level | The average range of pixel values in an image |
| Noise | Anything that distracts from the information required on an image |
| Nutating Detector Ring | When the detectors vibrate in such a way as to keep the detectors nearest the tube out of the way of the X-ray beam |
| Pitch | The table movement during one complete rotation of 360° divided by the column width (or slice thickness) |
| Example If the table moves 10 mm during one complete rotation and a beam width of 5 mm was used, the pitch value = 2 |
|
| Pixel | A two dimensional ‘picture cell’ or ‘dot’ that makes up the image on a digital display screen |
| Profile | Line of data |
| Slice | A section through the patient which is recorded when the X-ray tube and detector make one complete rotation |
| Slice Interval | The distance between reconstructed slices |
| Spatial Resolution | The smallest part of an image that can be seen |
| Translate | Movement in a horizontal direction |
| Voxel | A three dimensional pixel |
WindowThe range of colour (or grey) scale values displayed on a digital imageWindow WidthThe range of pixel values displayed in the digital image
| Gantry | A circular device for holding the detectors |
| X-ray Tube | A method of producing X-rays which are collimated so that they are aligned to a specific number of detectors |
| Detectors |
• A solid state device containing caesium iodide crystals which collects the amount of radiation transmitted through the patient
• Or UFCTM (Ultrafast Ceramic) LSO (Lutetium Oxyorthosilicate) crystal technology
|
| Photomultipliers |
• A device for increasing the number of electrons
• The photons from the detector hit a cathode which produces electrons which bombard plates and produce more electrons
• Used in earlier scanners – replaced by photodiodes
|
| Photodiode |
• Simply, a light controlled variable resistance
• When dark there is very little current flow
• But when the PN junction is exposed to light, current flows in direct proportion to the quantity of light it is exposed to
• Solid state devices coated with a fluorescent rare earth phosphor, smaller, more stable and more sensitive and a third of the size of photomultipliers
|
| Housing |
• A ‘doughnut’ shaped structure which contains the X-ray tube and the detectors
• With a patient opening (aperture) in the order of 70 cm diameter
|
| Movement |
• Originally high tension cables wound round a drum
• Disadvantages that the cables had to be ‘unwound’ after each cycle
• Replaced with slip ring and brushes
• Gives a constant electrical supply
• Therefore allows continual movement during rotations
|
| Table | For the patient to lie on and can move forward at a predetermined distance or at a constant speed to enable the next ‘slice’ to be taken |
| Operator Console | Where the operator can determine the settings for the scan |
| Display Station | For the viewing, analysis, networking and storage of the final image |
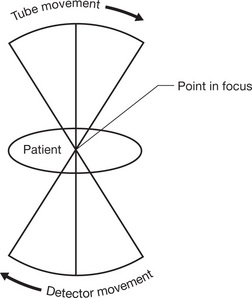
| Tomographic Principle |
• The X-ray tube and detector move together
• They rotate round a set point
• Structures above and below that point are ‘blurred’ due to the movement of the tube and detector
|
Fig. 14.1 The tomographic principle.
Tissue AttenuationAs different parts of the body have different densities they absorb radiation to different degreesAttenuation Coefficient
• Is the measure of the absorption of an X-ray beam along a specific path through a body or substance
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree