Disease site
Presentation
Recommended treatment
Pancreas
Resectable
Surgery +/− adjuvant chemoradiotherapy or chemotherapy
Borderline resectable (adequate KPS)
Neoadjuvant chemoradiation followed by restaging and resection if feasible
Borderline resectable (poor KPS) unresectable
Definitive chemoradiation, conventionally fractionated radiation alone, chemotherapy alone, or SBRT
Metastatic
Palliation with stents, surgical bypass, chemotherapy, RT, and supportive care as indicated; SBRT not indicated except for expedient palliation
Liver
Resectable HCC or oligometastatic disease with controlled primary
Partial hepatectomy
Unresectable/medically inoperable HCC or oligometastatic disease with controlled primary
Upfront Liver transplant
Restaging and resection if feasible following transarterial chemoembolization, radiofrequency ablation, cryotherapy, alcohol, SBRT, or sorafenib
Abdominal, retroperitoneal, and pelvic lymph nodes
Metastatic disease
Systemic therapy preferred, although surgery and SBRT should be discussed in oligometastatic settings or for palliation of pain
Adrenal glands
Metastatic disease
Systemic therapy preferred, although surgery and SBRT should be discussed in oligometastatic settings or for palliation of pain
Radiosurgical Technique
Simulation and Field Design
Gold seed marker (GSM) placement by EUS (pancreas) or CT-guidance (liver ) 1+ week prior to simulation to allow inflammation to subside.
Oral contrast 30–60 min prior to simulation , unless MRI used for planning.
Supine with arms above head and wingboard or alpha cradle to stabilize torso. Consider abdominal compression depending on image guidance modality.
Pancreas lies at L1-L2, celiac axis at T12, and SMA at L1.
Treatment planning:
Contrast-enhanced CT and/or MRI useful for delineating pancreatic tumor volume; triphasic CT and/or MRI for hepatic malignancies.
Image guidance:
Preferred: 4D-CT to define ITV with daily on-board imaging for set-up and tracking.
Acceptable: Active breathing control (ABC ), orthogonal MV imaging and kV fluoroscopy .
Field Design: ITV based on 4D-CT plus 3–5 mm margin.
Optimal: ITV based on 4D-CT plus 3–5 mm margin for PTV .
Other tracking/immobilization strategies typically require 5–7 mm radial and 1–1.5 cm craniocaudal expansions on GTV for adequate coverage.
Caution regarding inclusion of edema surrounding pancreatic tumor s due to excessively large field size.
Consider reducing PTV to allow for 2 mm margin to critical structures , especially in patients with poor performance status who are unlikely to tolerate exploratory laparotomy for bleeding , perforation, etc.
Avoid or minimize elective nodal stations in SBRT field due to toxicity.
Dose Prescription
Pancreas : 33 Gy in 5 fractions.
Liver: Based on location and underlying liver function .
Peripheral: 23–30 Gy in 1 fraction, 27.5–60 Gy in 3–6 fractions.
Central: 40 Gy in 5 fractions.
Abdominal lymph node s based on retrospective case series: 45–60 Gy in 3–6 fractions.
Adrenal metastases based on retrospective case series: 23 Gy in 1 fraction, 36 Gy in 3–5 fractions (Figs. 8.1 and 8.2).
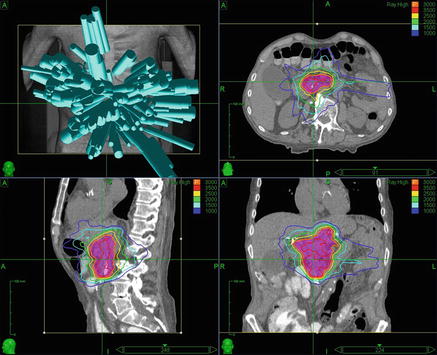
Fig. 8.1.
Pancreatic SBRT . 88-year-old male with locally advanced, unresectable pancreatic adenocarcinoma . A 4D CTV with an ITV expansion was used for treatment planning, which was carried out via robotic radiosurgery to a total dose of 3000 cGy in 5 fractions with 6 MV photons prescribed to the 73 % isodose line . Proceeding clockwise from the top left, beam angles, and axial, coronal, and sagittal CT images with isodose lines and the PTV in red color wash are shown
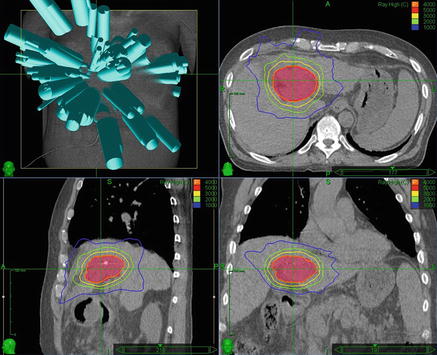
Fig. 8.2.
Liver SBRT . 61-year-old male with a history of hepatitis C and recurrent hepatocellular carcinoma of the porta hepatis status post transcatheter arterial chemoembolization on four occasions, and alcohol injection twice. A single intra-lesional fiducial marker was used for tracking during robotic radiosurgery . The tumor was treated to a total dose of 4000 cGy in 5 fractions with 6 MV photons prescribed to the 82 % isodose line . Proceeding clockwise from the top left, beam angles, and axial, coronal, and sagittal CT images with isodose lines and the PTV in red color wash are shown
Dose Limitations
Structure | Fractions | Constraints | Dose limiting toxicity | Study |
|---|---|---|---|---|
Stomach | 1 | V22.5 Gy < 4 % Distal lumen wall free from 50 % isodose line | Ulceration, fistula | Chang et al. Cancer 2009 |
3 | Dmax < 30 Gy | Kavanagh et al. IJROBP 2010 | ||
6 | Dmax < 32 Gy D3 cc < 36 Gy | |||
Small bowel | 1 | V12.5 Gy < 30 cc | Ulceration, fistula | Kavanagh et al. IJROBP 2010 |
3 | Dmax < 30 Gy | Bujold et al. JCO 2013 | ||
6 | Dmax < 36 Gy | Kavanagh et al. IJROBP 2010 | ||
Duodenum | 1 | V22.5% < 5 % V12.5 Gy < 50 % Distal lumen wall free from 50 % isodose line | Ulceration, fistula | Chang et al. Cancer 2009 |
6 | Dmax < 33 Gy D1 cc < 36 Gy | |||
Large bowel | 6 | Dmax < 36 Gy | Colitis, fistula | Bujold et al. JCO 2013 |
Liver | 1 | V5 Gy < 50 % V2.5 Gy < 70 % | Liver function, cirrhosis/hepatitis, biliary stricture, radiation-induced liver disease (RILD) | Chang et al. Cancer 2009 |
1, 3-5 | 700 cc < 15 Gy | |||
3-6 | HCC: MNLD < 13 Gy (3 fx), <18 Gy (6 fx) Metastases: MNLD < 15 Gy (3 fx), < 20 Gy (6 fx) | Pan et al. IJROBP 2010 | ||
5 | V30 Gy < 60 % V27 Gy < 70 % for cirrhosis/hepatitis | Katz et al. IJROBP 2007 | ||
6 | Vtot–V21 Gy > 700 cc | Tozzi et al. Rad Onc 2013 | ||
Kidney | 1 | V5 Gy < 75 % | Kidney function, malignant hypertension | Goodman et al. IJROBP 2010 |
6 | V15 Gy < 35 % Mean dose < 12 Gy | |||
Spinal cord | 1 | Dmax < 12 Gy | Myelitis | Goodman et al. IJROBP 2010 |
6 | Dmax < 18 Gy | |||
Chest wall | 3 | V30 Gy < 10 mL | Pain or fracture | Rusthoven et al. JCO 2009
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|