E
ear the sensory organ concerned with hearing and balance. It has three parts, the outer (external), middle (tympanic cavity) and inner (internal) ear. The outer ear comprises the auricle (pinna) and the external auditory canal along which sound waves pass to vibrate the tympanic membrane which separates it from the middle ear. The middle ear cavity is air-filled and contains three tiny bones or ossicles: malleus, incus and stapes. The ossicles transmit the sound waves to the inner ear via the oval window. The middle ear communicates with the nasopharynx via the eustachian tube (pharyngotympanic tube). The fluid-filled inner ear comprises the cochlea (organ of hearing) and the semicircular canals which are concerned with balance. The cochlea and semicircular canals contain the nerve endings of the cochlear and vestibular branches of the vestibulocochlear or auditory nerve (eighth cranial). See also cerumen, cochlea.
eardrum the tympanic membrane at the end of the external auditory canal. The first auditory ossicle is attached to the inner surface.
eating disorders a term used to describe the range of conditions in which an individual’s eating behaviour and nutrient intake is inappropriate for their needs. anorexia nervosa is characterized by distorted body image and a deliberate restriction of food intake, resulting in severe weight loss, malnutrition, endocrine disorders and electrolyte disturbances. bulimia nervosa – body weight is controlled by periods of restricted eating, purging and binge eating. Weight usually remains stable and within normal range. binge eating disorder – periods of binge eating without periods of food restriction or purging which result in the development of obesity. A complex mixture of social and psychological factors and life events predispose to and precipitate the development of eating disorders. Consequently they are best treated by a multidisciplinary team.
ecchondroma a benign tumour composed of cartilage which protrudes from the surface of the bone in which it arises.
ecchymosis bruise.
eccrine the most abundant type of sweat gland. See also apocrine glands.
echo the reflection of an ultrasound wave back to the transducer when the beam hits a surface at right angles.
echocardiography the use of ultrasound as a diagnostic tool for studying the structure and motion of the heart.
echoencephalography passage of ultrasound waves across the head. Can detect abscess, blood clot, injury or tumour within the brain.
echogenicity a characteristic of an ultrasound image, for example, benign masses are often homogeneous and malignant masses are often heterogeneous or fluid is black and solid areas appear white.
echo rephrasing the re-establishment of a magnetic resonance signal by either using a 180°radio frequency pulse or by gradient switching.
echo time (TE) the time between the centre of the excitation pulse and the peak of the echo.
echo train length the number of echoes that are individually phase encoded for a fast spin-echo sequence and corresponds to the number of lines of k-space measured per repetition time interval, they range from 3 to 128 depending on the type of pulse sequence. See also k-space, repetition time.
eclampsia occurrence of convulsions in a pregnant woman with signs of pre-eclampsia. A sudden convulsive attack.
ecmnesia impaired memory for recent events with normal memory of remote ones. Common in old age and in early cerebral deterioration.
ecological study a research study where a particular group of individuals rather than an individual, for example, schools, towns, etc., form the unit being observed.
economy describes spending or using as little as possible while still maintaining quality.
ectoderm the outer of the three primary germ layers of the early embryo. It gives rise to some epithelial and nervous tissues, for example, skin structures, inner ear, mammary glands, pituitary gland, the central nervous system, cranial, spinal and autonomic nerves, adrenal medulla and the lens and retina. See also endoderm, mesoderm.
ectogenesis (in vitro fertilization) the growth of the embryo outside the uterus.
ectopia malposition of an organ or structure, usually congenital.
ectopia vesicae an abnormally placed urinary bladder which protrudes through or opens on to the abdominal wall.
ectopic beat see extrasystole.
ectopic pregnancy (tubal pregnancy) pregnancy outside the womb (extra-uterine gestation), the uterine (fallopian) tube being the most common site.
ectrodactyly, ectrodactylia congenital absence of one or more fingers or toes or parts of them.
eczema an inflammatory skin reaction that may begin with erythema, then vesicles appear. These rupture, forming exudative areas that may crust. Scaling may occur. In chronic forms the skin becomes thickened. Some authorities limit the word ‘eczema’ to the cases with internal (endogenous) causes while those caused by external (exogenous) contact factors are called dermatitis. The skin of patients with eczema may be colonized or infected with Staphylococcus aureus. See also dermatitis.
eddy currents are induced electric currents in a transformer core and oppose the direction of the current in the windings of a transformer resulting in a power loss in the transformer, they can be reduced by laminating the core. In magnetic resonance imaging they are induced in the gradient coils or the structure of the magnet and degrade the image unless compensated for or eliminated.
edentulous without natural teeth.
editing altering a text or computer program.
effective current the value of current flowing for the same time that would produce the same electrical energy in a circuit as the equivalent alternating current.
effective dose a calculation to determine that amount of radiation received by a patient, for radiation protection purposes, which is weighted for each organ because different organs in the body show different sensitivity to radiation. The amount of a drug that can be expected to initiate a specific intensity of effect in people taking the drug.
effective half-life the time taken for the activity of a radionuclide in an organ to be reduced to half its original activity.
effective photon energy the energy of a homogeneous beam of photons having the same half value layer as the X-ray beam being evaluated.
effectiveness describes using resources to achieve the required outcomes.
effective voltage the value of voltage flowing for the same time that would produce the same electrical energy in a circuit as the equivalent alternating voltage.
effector a motor or secretory nerve ending in a muscle, gland or organ.
efferent carrying, conveying, conducting away from a centre. See also afferent.
efferent nerve one which conveys impulses outwards from the central nervous system to the muscles and glands. Also known as motor nerves.
effervescent material used in radiotherapy to make an immobilizing device by placing the patient on an empty polythene bag, introducing the self hardening material and producing an impression of the patient’s position, the impression can then be used during treatment to exactly replicate the patient position.
efficiency describes the use of minimum resources to achieve the maximum outcomes.
effusion extravasation of fluid into body tissues or cavities, such as a pleural effusion, or into joints where it causes swelling.
ejaculation sudden emission of semen from the penis at the moment of male orgasm. retrograde ejaculation a situation where semen is discharged backwards into the bladder. It may follow prostate surgery or be associated with diabetic neuropathy.
elastic collisions the mutual attraction of atoms, molecules etc. when the total energy is unchanged after the collision.
elastic scattering when a photon interacts with an electron, is deflected from its path but does not lose energy. See also coherent scattering.
elbow joint a synovial hinge joint formed by the humerus, radius and ulna.
elder abuse physical, sexual, psychological, pharmacological or financial abuse of older people. May be by family, neighbours or carers.
electric circuit the diagrammatic representation of electron flow through an electrical device.
Symbol and function of electric circuit elementsa
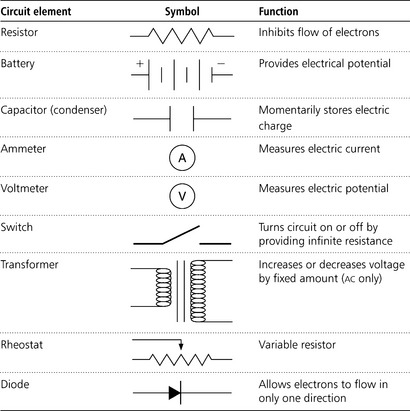 |
a From Radiologic science for technologists, 8th edn, 2005, S C Bushlong, Mosby, St Louis, with permission.
electric current the rate of flow of electrons in a material. An electric current of one ampere flows at a point if a charge of one coulomb flows past the point per second.
electric field the area surrounding an electrical charge, if an electric charge is placed inside the field a noticeable force will be exerted on it.
electrical potential at a point is the measure of the work required to bring a unit positive charge from infinity to that point.
electric shock shock caused when an electric current passes through the body, usually caused by accidental contact with an electric supply.
electrocardiogram (ECG) a recording of the electrical activity of the heart muscle during the cardiac cycle made by an electrocardiograph. The normal heart produces a typical waveform, sinus rhythm, which consists of five deflection waves, known universally as PQRST. See also ambulatory ECG, exercise (stress) ECG.
electrocardiograph an instrument that records the electrical activity of the heart from electrodes on the limbs and chest.
electrode in medicine or therapy, a conductor in the form of a pad or plate, whereby electricity enters or leaves the body.
electroencephalogram (EEG) a recording of the electrical activity of the brain, made by an electroencephalograph.
electroencephalograph an instrument by which electrical impulses derived from the brain can be amplified and recorded, in a fashion similar to that of the electrocardiograph.
electrolysis chemical decomposition by electricity, with ion movement shown by changes at the electrodes. Term used for the destruction of individual hairs (epilation), removal of moles, spider naevi, etc., using electricity.
electrolyte a solution of a substance, such as sodium chloride, which dissociates into ions with an electrical charge (anions, cations). In medicine it describes the individual ion, for example, potassium and bicarbonate ions in the body. electrolyte balance the balance of relative amounts of electrolytes, for example, potassium, sodium, magnesium, calcium, chloride, bicarbonate (hydrogen carbonate) and phosphate in blood, other fluids and tissues. The balance between ions with a positive charge and those with a negative charge ensures overall electrical neutrality in the body. Many conditions and diseases cause electrolyte imbalance, which is often associated with loss of fluid and pH homeostasis.
electrolytic recovery a method for recovering silver from radiographic fixer solution using a carbon anode and a stainless steel cathode, a direct current is passed between the two and the positively charged silver ions are attracted to the cathode where they are neutralized and form metallic silver, either a low or a high current density is used.
electromagnet is formed when a piece of soft iron is placed inside a solenoid resulting in induced magnetism within the iron bar.
electromagnetic radiation waves of energy that are caused by the acceleration of charged particles.
electromagnetic spectrum the ordering of electromagnetic radiation into the various wavelengths and frequencies.
The electromagnetic spectrum (not drawn to scale).
From Principles of radiological physics, 3rd edn, D T Graham, 1996, Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, with permission.
electromotive force (EMF) measures the force needed for an electric current to flow between two points. A derived SI unit (International System of Units), the volt (V), is used.
electron a negatively charged subatomic particle.
electron capture the capture of an electron by the nucleus of an atom, the electron combines with a proton to form a neutron and a neutrino which is ejected from the nucleus.
electron gun a piece of equipment that produces electrons by heating a spiral filament and then focussing them to form an electron beam.
electron microscopy the use of a beam of electrons to visualize very small structures, such as virus particles.
electron shells the orbits round the nucleus of an atom where the electrons are found in discrete levels, K is the nearest orbit to the nucleus and they are then labelled M, N, O, P etc.
electron transfer chain a series of mitochondrial oxidation-reduction reactions that generate cellular energy as ATP.
electron trap an area of low energy within a crystal which has the ability to catch and hold an electron for a period of time before it acquires the energy to escape.
electronic callipers a method of measurement used to calculate the distance between two points identified during ultrasound imaging.
electronic collimation used in PET cameras when an image is only recorded when two detectors simultaneously detect a photon of energy. See also positron-emission tomography.
electronic health record a computerized summary of a patient’s health record showing all their interactions with general practitioners and community healthcare workers.
electronic patient record a computerized summary of all a patient’s healthcare both in a primary and secondary care setting including written records, test results and medical images, for example, radiographs, scans, photographs, etc.
electronic portal imaging (EPI) a method of capturing an image digitally in real time and the image is superimposed on the original radiotherapy simulation film or image to verify the accuracy of the field placement.
electrophoresis a technique where charged particles are separated in a liquid medium by their characteristic speed and direction of migration in an electrical field. Used for measuring serum proteins.
element a substance that cannot be broken down by chemical means into any other substance, each atom in the element contains a specific number of protons in the nucleus, a variable number of neutrons in the nucleus and a given number of electrons outside the nucleus. One of the constituents of a compound. The elements are the primary substances which in pure form, or in combinations as compounds, constitute all matter.
elevation an upward movement such as the scapulae when the shoulders are lifted.
elimination the passage of waste from the body – urine and faeces.
ellipsoid joint a synovial joint that allows flexion, extension, abduction and adduction, for example, wrist joint.
eluting solution a liquid used to remove another substance by washing, used in a technetium generator where the eluting solution, saline, washes out the pertechnetate as sodium pertechnetate solution.
emaciation excessive leanness, or wasting of body tissue.
email an electronic mail system. Its current uses include sending imaging reports and pathology reports directly to GP surgeries from one computer to another via Healthlink. It may also be used by GPs for the direct referral of patients for examinations.
emasculation castration.
embolization the method of stopping, or drastically reducing the flow of blood in a vessel.
embolism obstruction of a blood vessel usually caused by a thrombus blood clot, but other causes include cancer cells, fat, amniotic fluid, gases, bacteria and parasites. Rarer emboli, such as fat, may follow long bone fractures, air may enter the circulation via a penetrating chest wound or during surgery, and amniotic fluid during labour. arterial embolism, originating from the left side of the heart or arterial disease, may travel to various sites including brain, bowel or limb; the effects dependent on the size of vessel affected and site, for example, gangrene of a limb or a portion of bowel. See also cerebrovascular accident, deep vein thrombosis, pulmonary embolism.
embolization therapeutic occlusion of a blood vessel using a foreign substance.
embolus solid body, for example a clot, or a gas bubble transported in the circulation. See also embolism.
embryo developmental stage starting 2 weeks after fertilization until the end of week 8 of gestation.
embryology study of embryonic development.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree