and Clarisse Dromain2
(1)
Department of Radiology, San Giovanni Hospital, Roma, Italy
(2)
Department of Radiology, Institut de Cancerologie Gustav Roussy, VilleJuif – Paris, France
Abstract
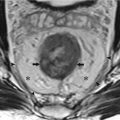
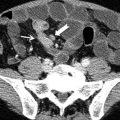
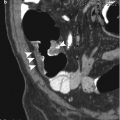
Endometriosis is a gynecologic disease consisting in ectopic foci of the endometrium with recurrent bleeding, and it is responsible of chronic pelvic pain in female. Ectopic endometrium frequently is located in the annex or along uterine ligaments and in the Douglas pouch. Other locations of pelvic endometriosis are represented by the rectovaginal septum, rectal wall, and sigmoid and small bowel serosa. In such cases endometriosis can present with small implants on the serosa or can evolve in chronic inflammatory disease followed by pelvic adhesion and fibrosis. In a more invalidating pattern called deep pelvic endometriosis, large fibrotic nodules or ill-defined fibrotic masses present an infiltrative pattern from the serosa to the muscular layer to the submucosa of the gut with possible luminal narrowing.
Endometriosis, GI
Endometriosis is a gynecologic disease consisting in ectopic foci of the endometrium with recurrent bleeding, and it is responsible of chronic pelvic pain in female. Ectopic endometrium frequently is located in the annex or along uterine ligaments and in the Douglas pouch. Other locations of pelvic endometriosis are represented by the rectovaginal septum, rectal wall, and sigmoid and small bowel serosa. In such cases endometriosis can present with small implants on the serosa or can evolve in chronic inflammatory disease followed by pelvic adhesion and fibrosis. In a more invalidating pattern called deep pelvic endometriosis, large fibrotic nodules or ill-defined fibrotic masses present an infiltrative pattern from the serosa to the muscular layer to the submucosa of the gut with possible luminal narrowing.
Pelvic MRI is the technique of choice in the assessment of pelvic endometriosis involving the gut, thanks to its ability to differentiate soft tissue. Usually deep pelvic endometriosis involving the gut presents at MRI a diffuse or focal infiltrative tissue with low signal intensity on T2-weighted images due to the predominant fibrotic components. However T1-weighted images with fat saturation are also useful to distinguish small high-signal foci within fibrotic tissue due to accumulation of hemoglobin degradation products. Laparoscopy represents the gold standard for pelvic endometriosis diagnosis allowing also treatments of adhesions and ablation of small peritoneal implants.
Enteric Cyst
Enteric cyst is a congenital cyst lined by gastrointestinal mucosa without bowel wall due to migration of small bowel or colonic diverticulum into the mesentery or mesocolon. Enteric cyst appears at cross-sectional imaging as a unilocular cystic mass with well-defined thin wall into the mesentery or mesocolon.
Enteritis
Enteritis is an inflammation of the small bowel commonly due to ingestion of food contaminated by pathogenic microorganism leading to abdominal pain, cramping, diarrhea, dehydration, and fever. Other forms of enteritis are represented by Crohn’s disease, enteric manifestation of vasculitis, and radiation-induced enteritis.< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree