and Sofia Gourtsoyianni2
(1)
UOC Radiologia BR, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata Verona, Verona, Italy
(2)
Imaging 2, Level 1, Lambeth Wing St Thomas’ Hospital, London, UK
Echinococcal Cyst (Hydatid Cyst)
It is a parasitic infection with Echinococcus granulosus. The infection occurs by direct contact with a dog (which is the final host, while sheep and cattle are the intermediate hosts) or via contaminated water or food. Embryos migrate through the intestinal mucosa and reach the liver through the portal vein. Cysts formed in the liver may grow 2–3 cm per year. When small, these are identical to simple liver cysts, while larger cysts form daughter cysts and membranes that can slough off or rupture. Pathognomonic imaging features are presence of calcifications seen in the capsule, best appreciated on CT (Fig. 1), or evidence of a floating membrane within ruptured lamellae (Fig. 2). The most severe complication is cyst rupture within the abdominal cavity.
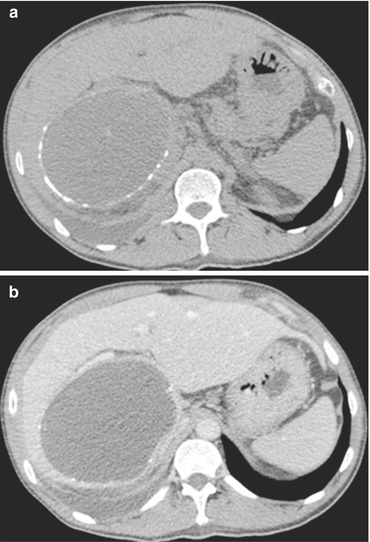
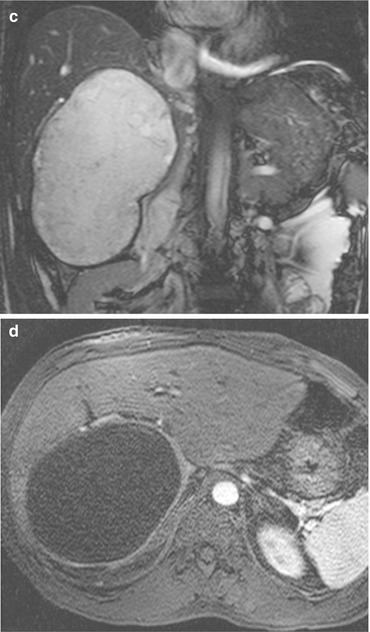


Fig. 1




Echinococcal cyst. Unenhanced (a) and venous phase (b) CT images show a large cystic lesion in the right liver lobe, with a thick enhancing wall with calcifications. Fluid content is hyperintense on coronal T2-w MRI (c). Wall enhancement is well depicted also in arterial post-Gd MRI (d)
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree