Ectopic Pancreatic Tissue
Brooke R. Jeffrey, MD
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Pancreatic tissue located outside normal confines of pancreas and lacking any anatomic or vascular connection with it
Imaging
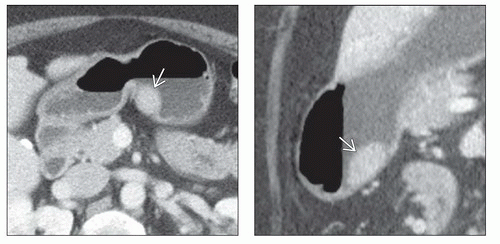
Diagnostic: Small intramural gastric mass with central umbilication (45%)
Central umbilication: Orifice of rudimentary duct within ectopic pancreas through which ectopic pancreatic tissue opens and drains into gastric lumen
Stomach: Typically 1-2 cm in diameter, along greater curvature or posterior aspect of antrum, within 6 cm of pylorus
Upper GI series may show narrowed pyloric channel ± polypoid or sessile mass
CT: Usually too small to be detected
Rarely intramural cystic collection in stomach and duodenum
Top Differential Diagnoses
Gastric ulcer
Round ulcer, smooth mound of edema, radiating folds to ulcer edge, Hampton line, ulcer collar
Gastric carcinoma
Polypoid or circumferential mass, ± ulceration, focal wall thickening with mucosal irregularity, focal infiltration of wall
Gastric metastases and lymphoma
“Bull’s-eye” sign: Ulceration in center of lesion
Gastric GIST
Large, lobulated, submucosal mass with ulceration; requires biopsy and histologic diagnosis
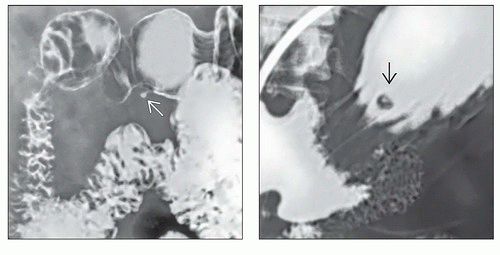 (Left) Upper GI series spot film shows a small antral mass with intact mucosa. A central “dot” of barium
 can be seen filling a rudimentary duct. (Right) Upper GI series spot film shows a small mass with central umbilication can be seen filling a rudimentary duct. (Right) Upper GI series spot film shows a small mass with central umbilication  . This is an unusual location for an ectopic pancreas. A “bull’seye” lesion of this type and location would raise concern for a metastatic lesion, Kaposi sarcoma, or lymphoma. . This is an unusual location for an ectopic pancreas. A “bull’seye” lesion of this type and location would raise concern for a metastatic lesion, Kaposi sarcoma, or lymphoma.Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|