Esophageal Metastases and Lymphoma
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Lymphoma: Malignant tumor of lymphocytes
Imaging
Ulcerated/polypoid mass of gastric cardia extending into distal esophagus
Top Differential Diagnoses
Intramural benign esophageal tumor
Esophageal carcinoma
Esophageal varices
Clinical Issues
Most common signs/symptoms
Dysphagia, weight loss, hematemesis, or asymptomatic
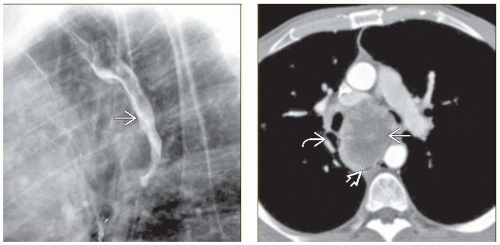
Esophageal metastases
Direct, lymphatic, or hematogenous spread
Direct invasion most common: Stomach carcinoma accounts for 50% of cases
Chemotherapy, surgical resection of complicating lesions (obstruction, upper GI bleed)
Complications
GI bleeding, perforation, obstruction
Prognosis
Usually poor
Treatment
Chemotherapy
Surgical resection of complicating lesions (obstruction, upper GI bleed)
Diagnostic Checklist
Check for history of primary cancer; biopsy required
Overlapping radiographic features of esophageal metastases, lymphoma, and primary carcinoma
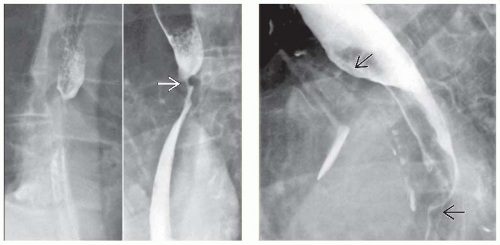
 (Left) Esophagram in a 70-year-old man with a history of known bladder carcinoma, now presenting with dysphagia, illustrates extrinsic or intramural involvement of the esophagus with eccentric narrowing of the lumen
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree


|