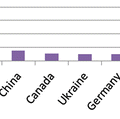
Fig. 11.1
CBRNE training for EU emergency medical services
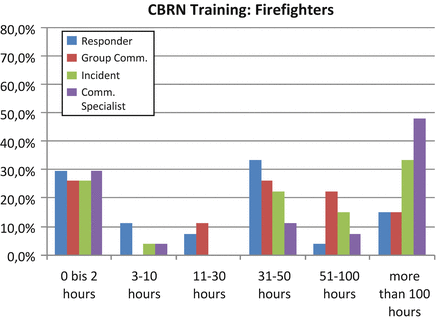
Fig. 11.2
CBRN training for EU firefighters
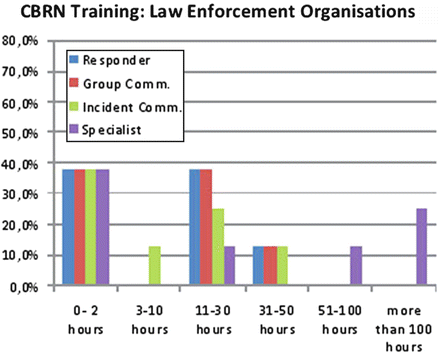
Fig. 11.3
CBRN training for EU law enforcement organisations
EU EMS: Basic CBRN training is provided only up to 10 h maximum; only specialists receive training exceeding 100 h.
EU Fire Fighters: CBRN training is typically provided for up to 50 h; specialists are trained for more than 100 h.
EU Law Enforcement Organisations: Basic CBRN training up to 50 h, but more than 100 h for specialists.
Significant deficits among EU FR were noted in the routine use of advanced IT-based tools and methods, such as:
Application of computer-based CBRN related modelling (e.g., toxic plume dispersion; impact of conventional explosives or nuclear weapons on structures and man);
Use of CBRN related information contained in an electronic database (e.g., concentration- and exposure limits);
Access to decision-aiding tools concerning CBRN related risk assessment (e.g., evacuation versus sheltering).
This frequently observable deficiency can contribute to an unnecessarily large number of victims among FR and members of the public alike in case of a CBRN incident.
11.2 EU Security Initiative
The European Commission (EC) has allocated € 1,350 million for security research in its wider R&D budget – referred to as the 7th Framework Programme for Research (FP7-SECURITY) – for the period 2007–2013. The main topics are: Security of the Citizen; Security of infrastructures and utilities; Intelligent surveillance and border security; Restoring security and safety in case of crisis; Security systems integration, interconnectivity and interoperability; Security and society; Security research, coordination and structuring. This includes advanced research into the societal dimension of security, protection of citizens against man-made and natural disasters, critical infrastructure protection, crisis management capabilities, intelligent maritime and land border surveillance, pre-standardisation and the interoperability of systems. However, out of the more than 400 security-related R&D projects only 13 projects address CBRN threats [4]. Table 11.1 below summarizes the main characteristics of these EC co-funded FP7-projects. The total cost for these projects amounts to € 84,308,982.
Table 11.1
FP7 security research projects related to radiological and nuclear threats
Project acronym | Full title | Coordinator | Total cost (EUR) |
|---|---|---|---|
Analytical methods | |||
MIRACLE | Mobile laboratory capacity for the rapid assessment of CBRN threats located within and outside the EU | Universite Catholique de Louvain (Belgium) | 1,420,617 |
SLAM | Standardisation of laboratory analytical methods | Uema Universitet (Sweden) | 1,320,763 |
GIFT CBRN | Generic integrated forensic toolbox for CBRN incidents | Netherlands Forensic Institute (The Netherlands) | 7,125,972 |
Protection of drinking water | |||
SECUREAU | Security and decontamination of drinking water distribution systems following a deliberate contamination | Université de Lorraine (France) | 7,462,072 |
SAFEWATER | Innovative tools for the detection and mitigation of CBRN related contamination events of drinking water | Arttic (France) | 4,814,570 |
Countermeasures | |||
COUNTERFOG | Device for large scale fog decontamination | Universidad Carlos III de Madrid (Spain) | 4,407,528 |
IF REACT | Improved first responder ensembles against CBRN terrorism | Universite Paris XII – Val de Marne (France) | 5,243,368 |
PRACTICE | Preparedness and resilience against CBRN terrorism using integrated concepts and equipment | Uema Universitet (Sweden) | 11,691,686 |
CATO | CBRN crisis management: architecture, technologies and operational procedures | NESS (Israel) | 14,055,519 |
CBRNEMAP | Road-mapping study of CBRNE demonstrator | Uema Universitet (Sweden) | 1,662,022 |
CAST | Comparative assessment of security-centered training curricula for first responders on disaster management in the EU | Paris-Lodron Universität Salzburg (Austria) | 2,858,318 |
Interoperability | |||
DESTRIERO | A decision support tool for reconstruction and recovery and for the interoperability of international relief units in case of complex crises situations, including CBRN contamination risks | E-GEOS SPA (Italy) | 4,171,403 |
BRIDGE | Bridging resources and agencies in large-scale emergency management | SINTEF ICT (Norway) | 18,075,144 |
11.2.1 Analytical Methods
In order to accelerate risk assessment and risk management it is essential to identify a CBRN agent as quickly as possible. Ability to analyze a suspected or proven hazardous agent fast and reliable is key in deciding on any further actions, whether it is protective measures for FR and members of the public, security actions or political decisions. In the ranking of priorities about 12 % of the total co-funding of CBRN FP7 projects focuses on the development of innovative analytical methods for such materials.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree