and Sofia Gourtsoyianni2
(1)
UOC Radiologia BR, Azienda Ospedaliera Universitaria Integrata Verona, Verona, Italy
(2)
Imaging 2, Level 1, Lambeth Wing St Thomas’ Hospital, London, UK
Fibrocystic Liver Diseases
Fibrocystic liver diseases, or ductal plate malformations, are a group of congenital diseases resulting from abnormal embryogenesis of the biliary ductal system.
The abnormalities include choledochal cyst, Caroli’s disease and Caroli’s syndrome, adult autosomal dominant polycystic liver disease and biliary hamartoma.
Fibrolamellar Carcinoma (FLC)
Fibrolamellar carcinoma is a rare liver malignancy, presenting in a younger population of patients without evidence of hepatitis or cirrhosis. It is a well-defined, nonencapsulated, large, solitary lesion with expansile growth pattern and lobulated margins. It may contain calcifications and present with a central scar that is hypointense on T1-w images, hypo/hyperintense on T2-w images and hypovascular on equilibrium phase. Differential diagnosis has to be made from FNH. Fibrolamellar carcinoma demonstrates heterogeneous arterial enhancement with isointensity or slight persistent hyperintensity in the delayed phase due to abundant fibrous tissue within the lesion (Fig. 1). With hepatocyte-specific contrast agents, FLC does not show significant enhancement and thus may be differentiated from FNH. Regional abdominal lymph nodes may be present.
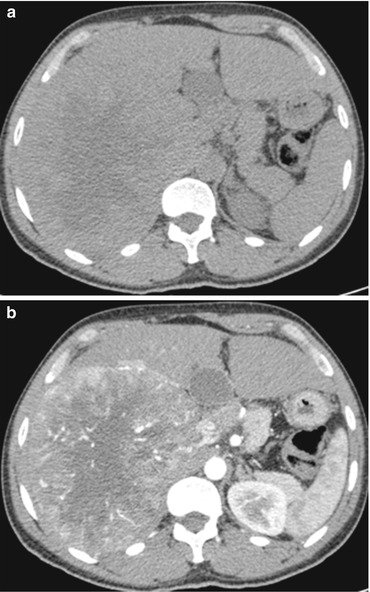
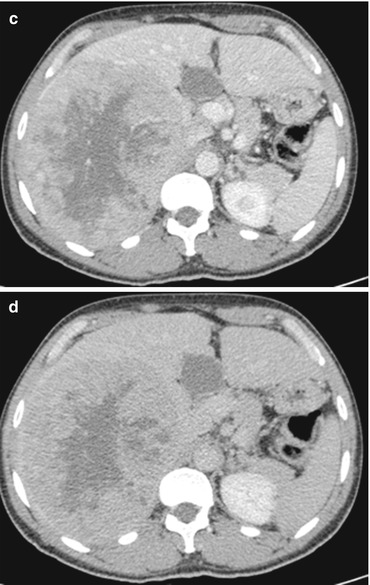


Fig. 1
Fibrolamellar carcinoma. A large lesion occupies the right liver lobe, inhomogeneously hypodense on non-contrast CT (a), with heterogeneous arterial enhancement (b), and isodense on venous (c) and delayed-phase images (d)
Focal Fatty Change (Liver)
Uneven or focal distribution of fat is common in the liver and may present both as fatty sparing and as focal fatty infiltration.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree