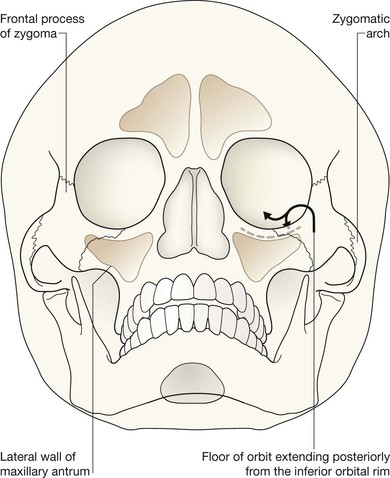
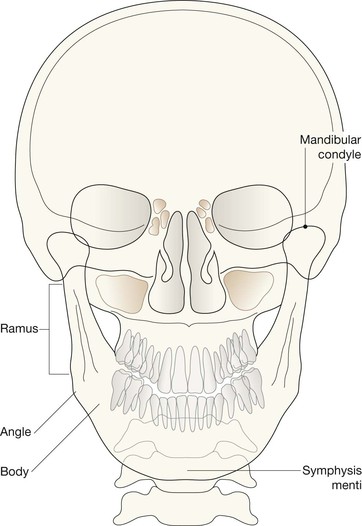
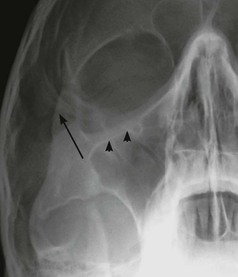
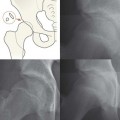
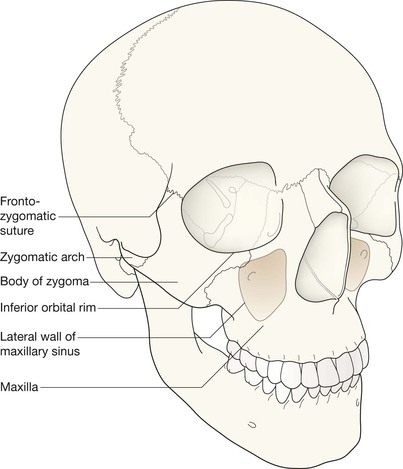
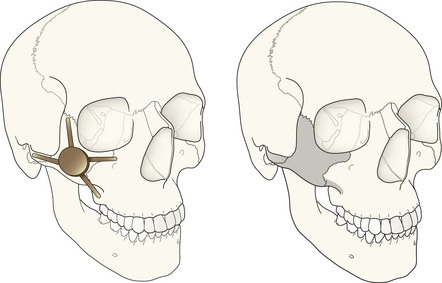
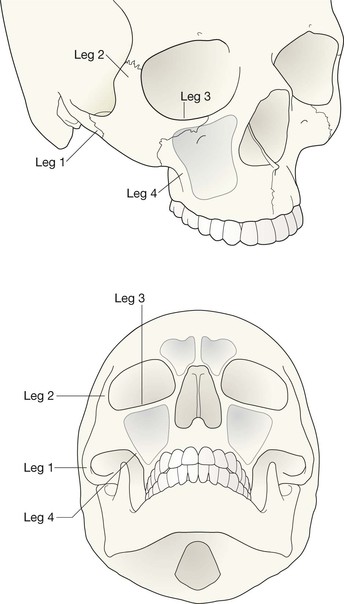
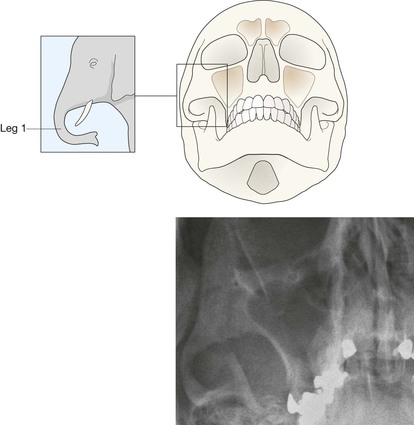
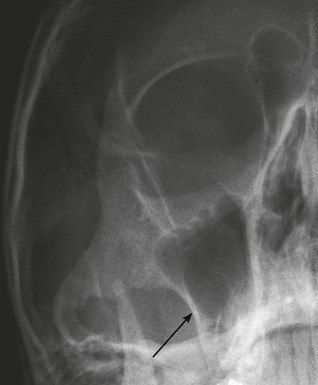
Midface and Orbit: one or two OM views; occasionally with a lateral view. Mandible: OPG, preferably with a PA view. Facial bone anatomy The orthopantomogram (OPG) The OPG is a technique for demonstrating the mandible, temporomandibular joints and teeth in a single plane. The X-ray tube and the film cassette rotate around the patient and the exposure lasts a few seconds. A panoramic image is obtained. The temporomandibular joint (TMJ) The midface anatomy appears very complex. Try this approach. Think of the zygoma (malar bone) as a midface stool with four legs. The seat of the stool is very strong. The four legs are much weaker, so you need to assess each leg very carefully. Inspect the OM views as follows: Concentrate on the stool’s legs. For each leg compare the injured side with the other (normal) side. Look for any asymmetry or any difference between the appearance of the matching legs. Check as follows: 2. Leg 2: frontal process of the zygoma. 4. Leg 4: lateral wall of the maxillary antrum. 5. Look for fractures and look for: □ a fluid level (blood from a fracture) in the maxillary antrum; Always apply this rule: If any one of the legs is fractured then always, always, double check whether the other three legs of the midface stool are intact (see Tripod fracture, p. 63). Midface stool—Leg 1 The zygomatic arch. The arch is easy to identify on the OM view, where it may be likened to an elephant’s trunk. This is a frequent site of fracture, either as an isolated injury or as part of a tripod fracture. This radiograph is normal. Potential pitfall: The normal elephant’s trunk often has a normal developmental bump on its inferior surface, about half way along the trunk. Midface stool—Leg 4 Lateral wall of the maxillary antrum (arrow). Normal radiograph. Why we do not refer to Le Fort fracture patterns Fractures of the middle third of the face are often classified according to the Le Fort fracture patterns3,4,10–13. This is a useful classification for the maxillofacial surgeon when planning treatment. However, the Le Fort patterns are not particularly helpful when carrying out a step-by-step assessment of the plain radiographs in the Emergency Department. This is because the Le Fort patterns involve the pterygoid plates and the precise detail is only reliably provided by a CT scan with reconstruction of the CT images13. Designating a precise Le Fort injury pattern (if present) is at best guesswork when assessing plain radiographs.
Face
Normal anatomy: midface & orbit
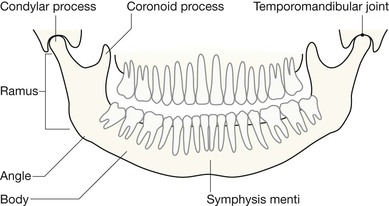
Normal anatomy: mandible
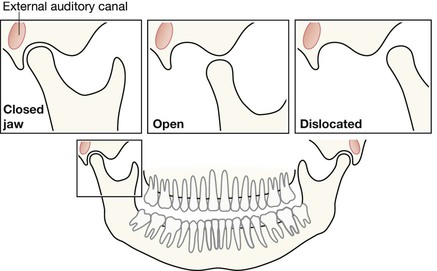
Analysis: the checklists
Midface injury
A five-point checklist
The common injuries
Related posts:
![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree