KEY FACTS
Terminology
- •
Focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH)
- •
Benign tumor of liver caused by hyperplastic response to localized vascular abnormality
Imaging
- •
US
- ○
Usually homogeneous and isoechoic
- ○
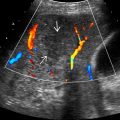
Spoke-wheel pattern on color Doppler US
- –
Large central feeding artery with multiple small vessels radiating peripherally
- –
- ○
- •
CEUS/CT/MR
- ○
Bright, homogeneously enhancing mass in centrifugal direction on arterial phase (CEUS) with delayed enhancement of central scar (CT/MR)
- ○
- •
Gadoxetate-enhanced MR
- ○
Most specific test to diagnose FNH
- ○
Prolonged enhancement of entire FNH on hepatobiliary phase scan
- ○
Top Differential Diagnoses
- •
Hepatic adenoma
- •
Fibrolamellar hepatocellular carcinoma
- •
Hepatic cavernous hemangioma
- •
Hypervascular metastasis
Pathology
- •
Normal hepatocytes and malformed bile ductules
- •
Thick-walled arteries in fibrous septa radiating from center to periphery
Clinical Issues
- •
Common in young to middle-aged women
- •
Excellent prognosis
Diagnostic Checklist
- •
Imaging is more reliable than histology in making diagnosis of FNH
Scanning Tips
- •
Look for radiating vessels that flow in centrifugal direction (away from center) with color Doppler
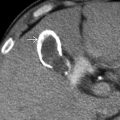
 with a central scar and thin, radiating septa dividing the mass into hyperplastic nodules. Note the cluster of small arteries near the central scar.
with a central scar and thin, radiating septa dividing the mass into hyperplastic nodules. Note the cluster of small arteries near the central scar.
 , typical of focal nodular hyperplasia. (Courtesy M. Yeh, MD, PhD.)
, typical of focal nodular hyperplasia. (Courtesy M. Yeh, MD, PhD.)
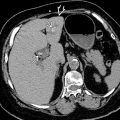
 . The mass causes contour deformity and mass effect upon the adjacent gallbladder and portal vein
. The mass causes contour deformity and mass effect upon the adjacent gallbladder and portal vein  . The lesion is difficult to distinguish from the surrounding liver, earning its moniker “stealth lesion.”
. The lesion is difficult to distinguish from the surrounding liver, earning its moniker “stealth lesion.”
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree