Foot Vessels
IMAGING ANATOMY
Arteries
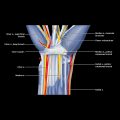
 Dorsal artery of foot
Dorsal artery of foot
 Direct continuation of anterior tibial artery, changing name at ankle joint
Direct continuation of anterior tibial artery, changing name at ankle joint
 Course and relations
Course and relations
 Main branches
Main branches
 Arcuate artery: Arises at medial cuneiform level and runs laterally over metatarsal bases, deep to extensor tendons; gives off branches to metatarsals and toes
Arcuate artery: Arises at medial cuneiform level and runs laterally over metatarsal bases, deep to extensor tendons; gives off branches to metatarsals and toes
 1st dorsal metatarsal artery: Arises just before dorsalis pedis dives deep into sole
1st dorsal metatarsal artery: Arises just before dorsalis pedis dives deep into sole
 Continuation of calf vessel by same name, branch of popliteal artery
Continuation of calf vessel by same name, branch of popliteal artery
 Runs in tarsal tunnel behind and below medial malleolus accompanied by tibial nerve
Runs in tarsal tunnel behind and below medial malleolus accompanied by tibial nerve
 Divides into terminal branches (medial and plantar arteries) in tarsal tunnel
Divides into terminal branches (medial and plantar arteries) in tarsal tunnel
 Medial plantar artery is smaller
Medial plantar artery is smaller
 Lateral plantar artery is much larger than medial
Lateral plantar artery is much larger than medial