Fundoplication Complications
Michael P. Federle, MD, FACR
Key Facts
Terminology
Nissen FDP: Complete (360°) FDP
Toupet FDP: Partial (270°) FDP, posterior side
Belsey Mark IV repair: 240° FDP wrap around left lateral aspect
Imaging
“Wrap” complications
Tight FDP wrap (fixed narrowing and delayed emptying of esophagus)
Complete disruption of FDP sutures (recurrent hernia and reflux)
Partial disruption of FDP sutures (1 or more loose-looking outpouchings of wrap)
Complete wrap may slide downward over stomach; “hourglass” configuration of stomach
Intrathoracic migration of wrap upward through hiatus
Fluid collections in abdomen or mediastinum
Herniated abdominal fluid, lymph, hematoma, infection ± leak, abscess
Videofluoroscopic contrast-enhanced esophagram soon after surgery
Structural information, anatomical abnormalities
“Wrap” complications, leaks, persistence of reflux
CT for severe abdominal/chest pain, suspected visceral injury, or abscess
Top Differential Diagnoses
Postoperative edema
Plication defect
Extragastric complications
Diagnostic Checklist
Postoperative fluoroscopic evaluation should be used liberally or even routinely
CT for suspected leak or bleeding
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Fundoplication (FDP)
Definitions
Complications of anti-reflux surgery for management of gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD)
Nissen FDP: Complete (360°) FDP
Approach: Laparoscopic or open FDP
Gastric fundus wrapped 360° around intraabdominal esophagus to create antireflux valve
Concomitant diaphragmatic hernia reduced; diaphragmatic esophageal hiatus sutured
Toupet FDP: Partial (270°) FDP
Posterior hemivalve created
Belsey Mark IV repair: Open surgical; 240° FDP wrap around left lateral aspect of distal esophagus
Fundus sutured to intraabdominal esophagus; acute esophagogastric junction angle (angle of His)
Can also be performed via minimally invasive techniques
IMAGING
General Features
“Wrap” complications
Slipped or misplaced FDP
FDP disruption or breakdown
FDP herniation with intrathoracic migration
Too tight, too loose, or too long FDP
Herniation of stomach through diaphragmatic hiatus
“Nonwrap” complications
Injury to intraabdominal, intrathoracic organs
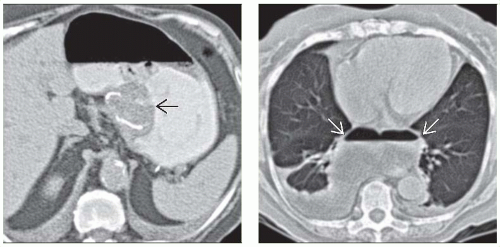
Leaks: Intraabdominal, intrathoracic
Mediastinal collection of gas and fluid (blood, transudate, or pus)
Fistulas; gastropericardial, gastrobronchial, etc.
Pneumothorax, pneumonia, pancreatitis, incisional hernia, mesenteric and portal venous thrombosis
Late complications
Recurrent paraesophageal herniation
Distal esophageal stricture
Radiographic Findings
Fluoroscopy
Normal postoperative appearance
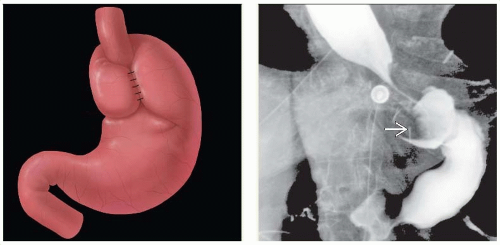
Nissen FDP wrap: Well-defined “mass” in gastric fundus; smooth contour and surface
Distal esophagus tapers smoothly through center of symmetric compression by wrap
Pseudotumoral defect of gastric fundus; part of fundus wrapped around distal esophagus
Defect more pronounced for complete wrap of Nissen than partial wrap of Toupet, Belsey
Belsey Mark IV repair
Wrap produces smaller defect than Nissen FDP
2 distinct angles form as esophagus passes FDP
Shallow upper angle; where esophagus, fundus, and diaphragm sutured together
Steep lower angle; where stomach pulled upward
“Wrap” complications