and Clarisse Dromain2
(1)
Department of Radiology, San Giovanni Hospital, Roma, Italy
(2)
Department of Radiology, Institut de Cancerologie Gustav Roussy, VilleJuif – Paris, France
Abstract
Gallstone ileus represents up to 5 % of small bowel obstruction more frequent in women over 60 years old with previous gallbladder disease. Small bowel obstruction in gallstone ileus is due to the impaction of a big gallbladder stone along the small bowel loops after a migration of gallstone from the gallbladder to the intestine through a bilioenteric fistula.
Gallstone Ileus
Gallstone ileus represents up to 5 % of small bowel obstruction more frequent in women over 60 years old with previous gallbladder disease.
Small bowel obstruction in gallstone ileus is due to the impaction of a big gallbladder stone along the small bowel loops after a migration of gallstone from the gallbladder to the intestine through a bilioenteric fistula.
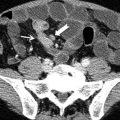
CT sign can depict indirect sign of bilioenteric fistulas such as gas in biliary tree and collapsed gallbladder and can directly depict the presence of a calcified gallstone at the transition zone (Fig. 1).
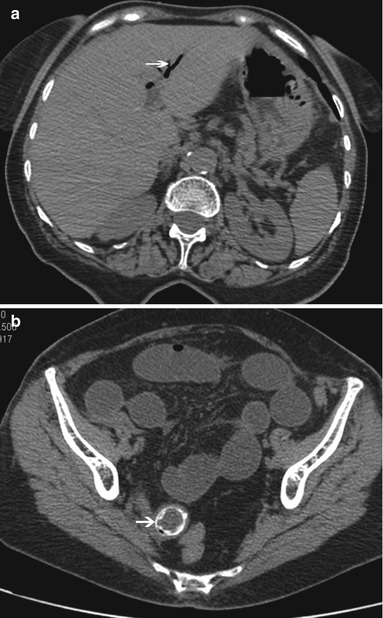
Fig. 1
CT images in a patient suffering with gallstone ileus. In (a) gas in the biliary duct is clearly visible (arrow); in (b) a calcified gallstone is visible in a pelvic small bowel loop with dilatation of upstream loops
Gas in Portal Vein
Gas in portal vein should be considered a life-threatening event and sign of bowel infarction and gangrene until proved otherwise.
Pathogenesis is due to intestinal wall alteration permitting passage of air into venules. The intestinal ischemia is the most common cause of gas in the portal venous system. However other possible causes are represented by ulceration of gastric or duodenal wall, iatrogenic air distension of the gastrointestinal system (ERCP, colonoscopy), or intra-abdominal sepsis (gas from septicemia in branches of mesenteric veins).
CT imaging is able to distinguish small amount of gas into tubular areas in the liver periphery as well as in portal and mesenteric veins. Main differential diagnosis is with pneumobilia (air located centrally in the liver within the bile ducts at the hilus and mainly in the left liver lobe).
Gastrografin®
Gastrografin is the brand name of an iodinated oral contrast medium (diatrizoic acid) with high osmolarity administered orally or by enema to image the gastrointestinal system in patients with contraindications for barium sulfate. Thanks to its high osmolarity, it shows cathartic properties and it was proposed as tagging agent for fluid residual stool in the colon prior to virtual colonoscopy.
Giardiasis
Giardiasis is a parasitic infection due to overgrowth of commensal parasite (Giardia lamblia) occurring in predisposed subject (altered immune mechanism). At histology giardiasis presents with blunted villi and cellular infiltrate of lamina propria and may be confused with celiac disease. Clinical feature widely ranges from symptomatic to severe diarrhea. Infection is commonly located in the duodenum and jejunum with thickened and distorted fold with normal ileum. Diagnosis is based on detection of Giardia lamblia cyst in formed feces or trophozoites in diarrheal stools.< div class='tao-gold-member'>Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree