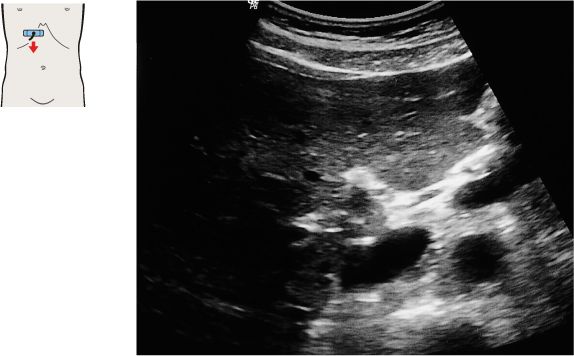
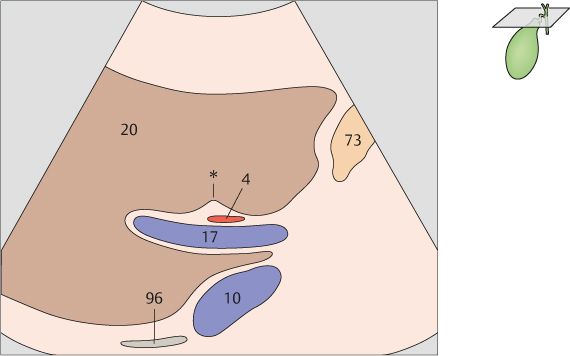
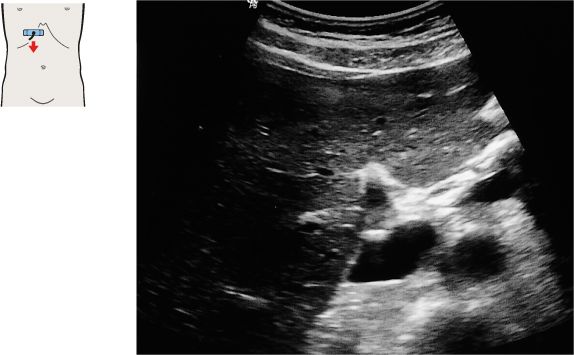
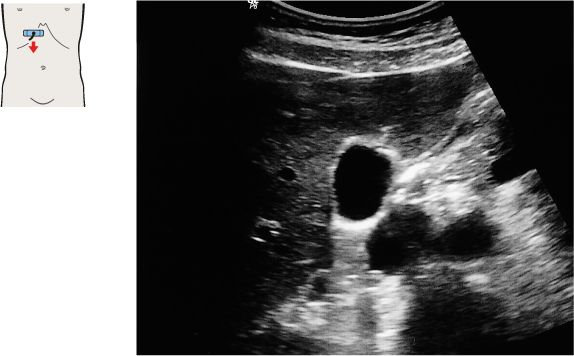
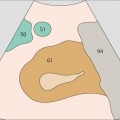
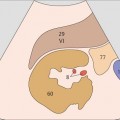
101 Right branch of the portal vein, ligamentum venosum
102 Portal vein, ligamentum venosum
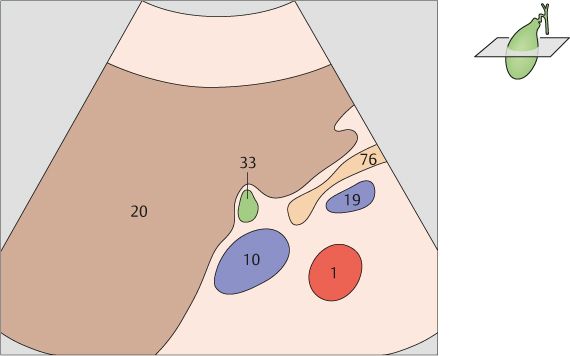
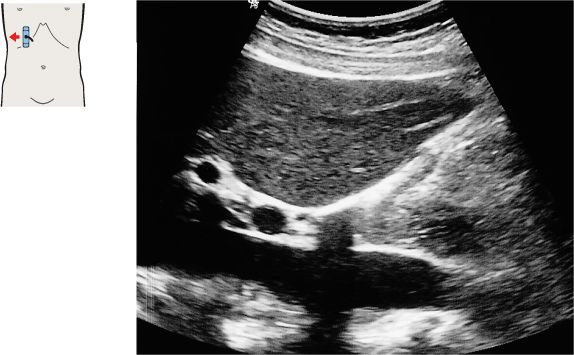
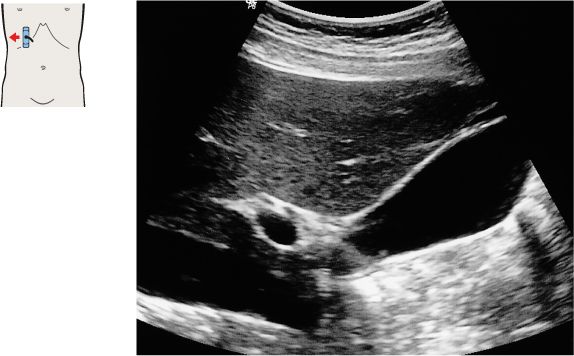
The interlobar fissure (*) anterior to the right branch of the portal vein is the key landmark for locating the gallbladder.
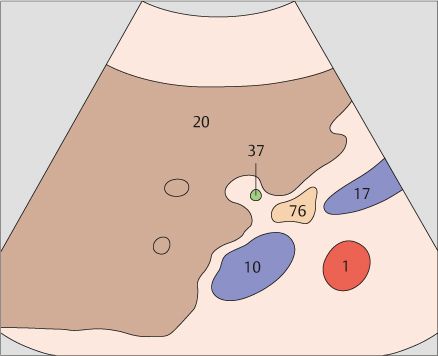
The gallbladder neck is located just caudal to the right portal vein branch and interlobar fissure.
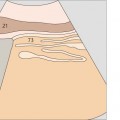
103 Neck of the gallbladder
104 Junction of the neck and body of the gallbladder
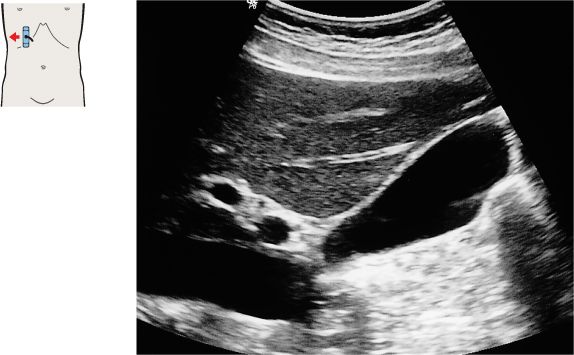
The duodenum is located medial to the neck of the gallbladder.
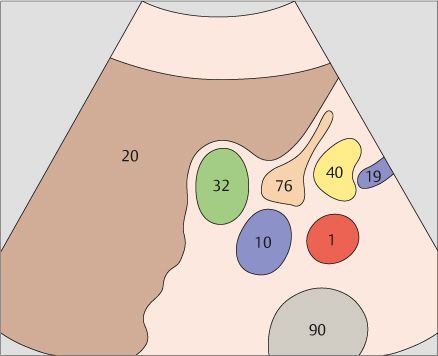
The duodenal bulb can be consistently identified on the free peritoneal side of the body or neck of the gallbladder.
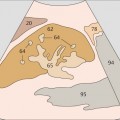
105 Body of the gallbladder
106 Gallbladder fundus
The duodenum passes between the body of the gallbladder and the vena cava.
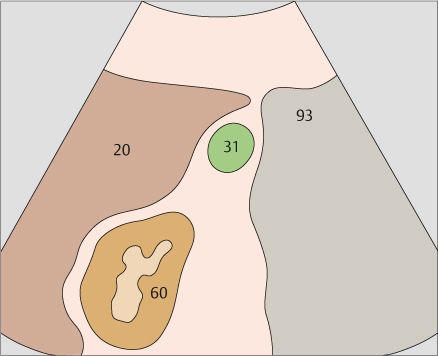
The gallbladder fundus may extend almost to the anterior wall of the trunk, or it may be situated very deeply behind the liver.
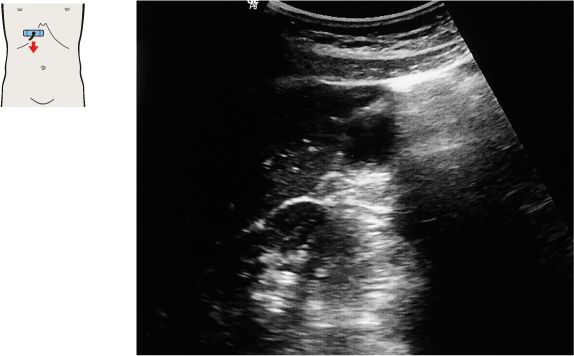
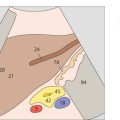
107 Vena cava, duodenum, portal vein bifurcation
108 Body of the gallbladder, portal vein bifurcation
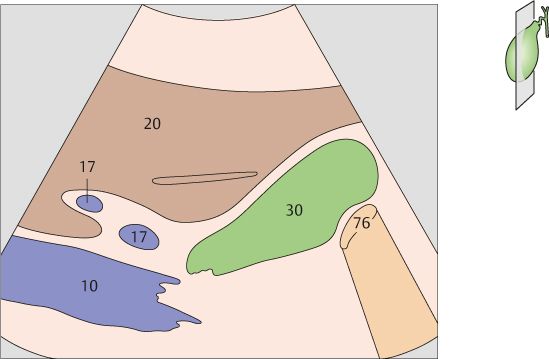
The vena cava, the portal vein bifurcation, and the echogenic band of the interlobar fissure are the principal landmarks for locating the gallbladder in longitudinal scans.
The duodenum is located posterior to the gallbladder and caudal to the right colic flexure.
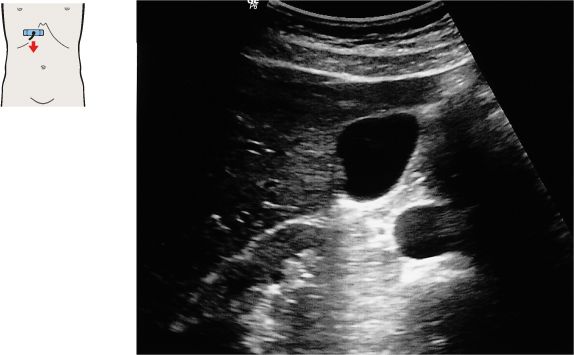
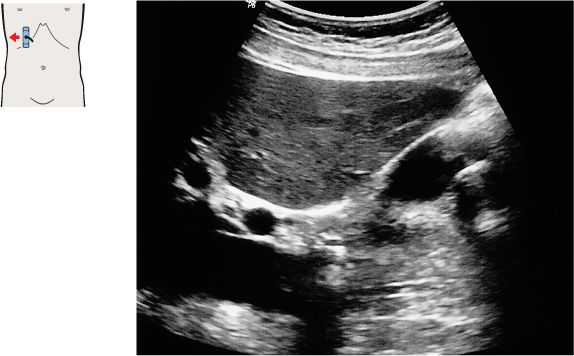
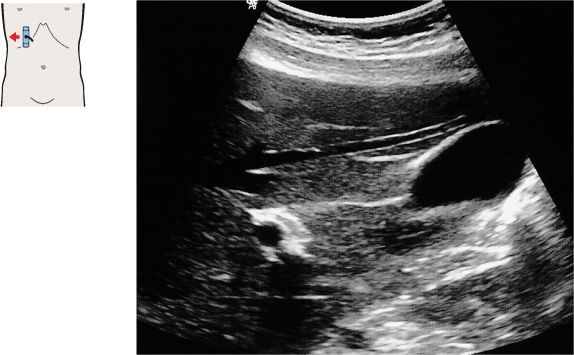
109 Gallbladder, portal vein
110 Gallbladder, portal vein
The shape and location of the gallbladder are highly variable. But the gallbladder neck is always located in the porta hepatis, caudal to the right branch of the portal vein.
The healthy gallbladder is a fluid-filled organ, usually pear-shaped, that does not contain internal echoes.
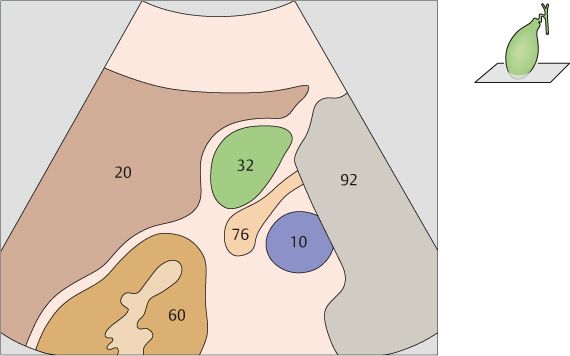
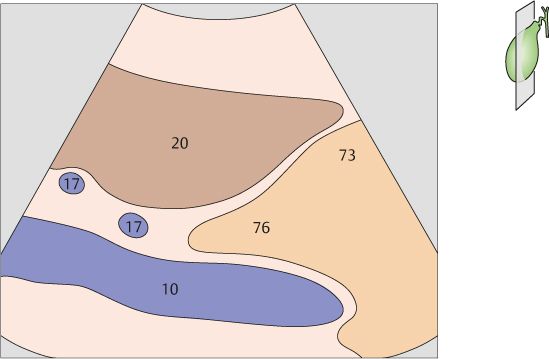
111 Gallbladder, portal vein, right kidney
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree