Ganglion Cyst
KEY FACTS
Imaging
IMAGING
General Features
 Dorsal wrist ganglia
Dorsal wrist ganglia
 Volar wrist ganglia
Volar wrist ganglia
 Finger
Finger
 Acromioclavicular joint
Acromioclavicular joint
 Shoulder
Shoulder
 Lumbar facet joints (not usually demonstrable by US)
Lumbar facet joints (not usually demonstrable by US)
 Hip: Anterosuperior, usually associated with labral tear
Hip: Anterosuperior, usually associated with labral tear
 Knee
Knee
 Proximal tibiofibular joint
Proximal tibiofibular joint
 Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis
Distal tibiofibular syndesmosis
 Foot and ankle: Cuneonavicular joint, intercuneiform joint, subtalar joint, talonavicular joint
Foot and ankle: Cuneonavicular joint, intercuneiform joint, subtalar joint, talonavicular joint
Ultrasonographic Findings
 Typical location
Typical location
 Elongated neck allows cyst to surface at distance from joint of origin
Elongated neck allows cyst to surface at distance from joint of origin
 ± multiloculated ± thin septations
± multiloculated ± thin septations
 ± small comet-tail artifacts due to colloid aggregates
± small comet-tail artifacts due to colloid aggregates
 ± inflammatory exudate: Inflammatory content of joint can extend into ganglia
± inflammatory exudate: Inflammatory content of joint can extend into ganglia
 Not compressible
Not compressible
 No hyperemia except with recent leakage when surrounding tissues may be mildly hyperemic and edematous
No hyperemia except with recent leakage when surrounding tissues may be mildly hyperemic and edematous
 Check for compression of small nerves, such as posterior interosseous nerve or superficial branch of radial nerve
Check for compression of small nerves, such as posterior interosseous nerve or superficial branch of radial nerve
Ganglion Cyst









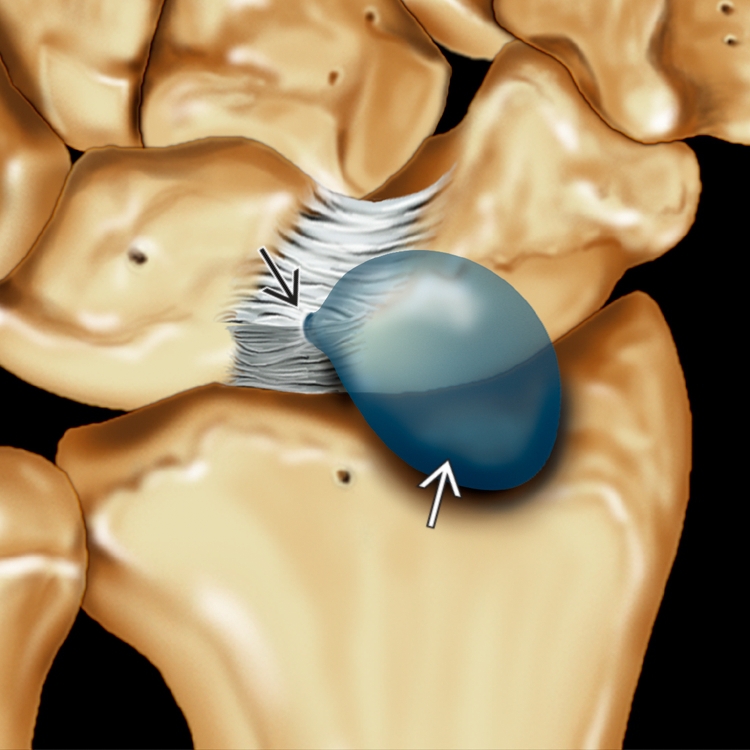
 arising from a defect in the dorsal capsule of the scapholunate ligament
arising from a defect in the dorsal capsule of the scapholunate ligament  . The ligament remains functionally intact.
. The ligament remains functionally intact.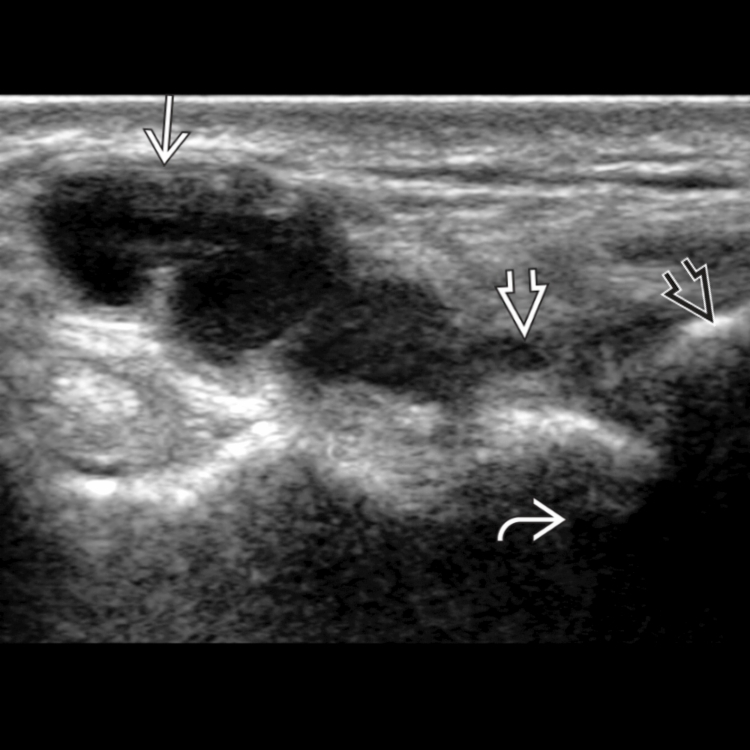
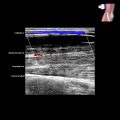
 in the dorsal aspect of the wrist. The stalk of the ganglion
in the dorsal aspect of the wrist. The stalk of the ganglion  extends toward the articulation between the scaphoid
extends toward the articulation between the scaphoid  and the distal radius
and the distal radius  .
.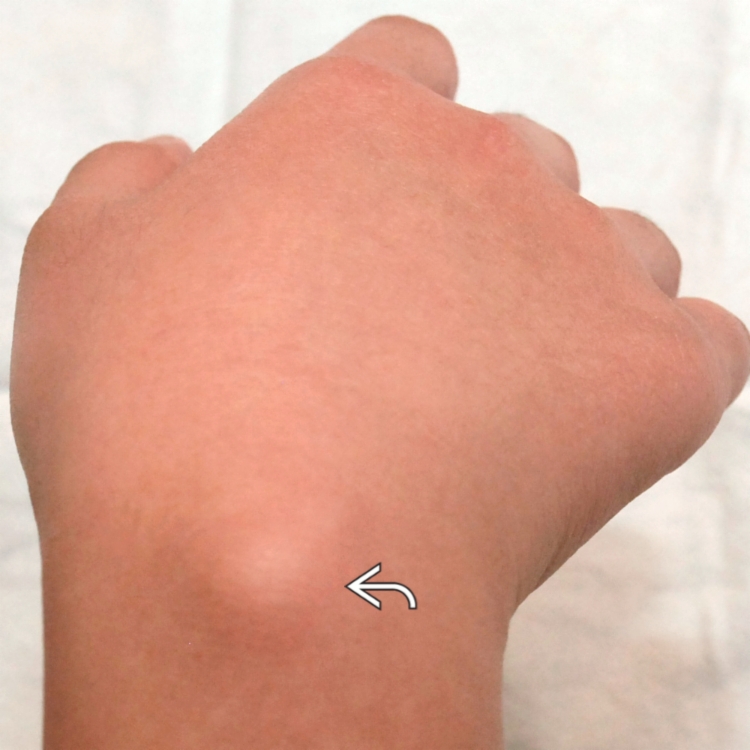
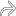 suggestive of a ganglion cyst.
suggestive of a ganglion cyst.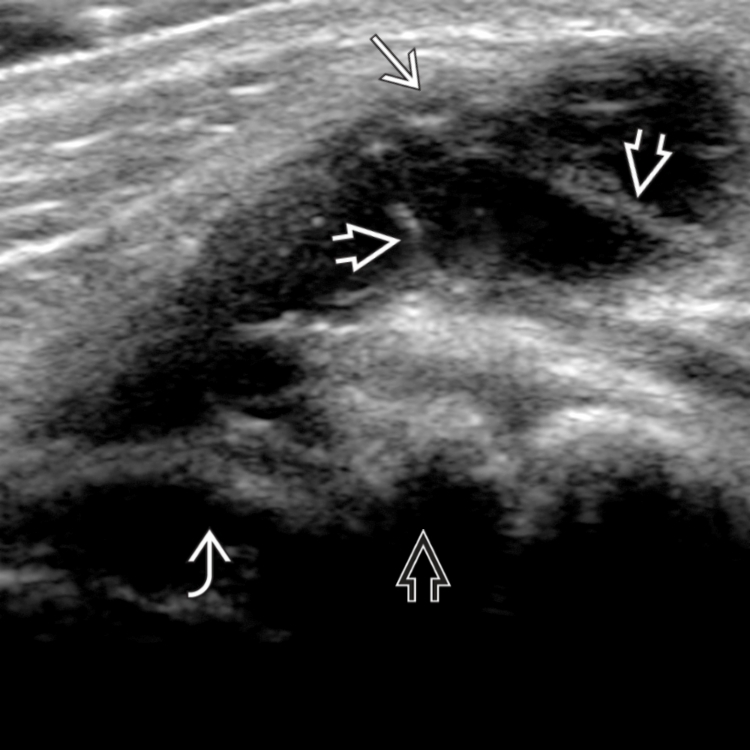
 arising from the dorsal aspect of the radioscaphoid articulation. There is mild septation
arising from the dorsal aspect of the radioscaphoid articulation. There is mild septation 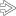 within the ganglion. The radial epiphysis
within the ganglion. The radial epiphysis  and scaphoid
and scaphoid 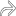 are shown. The small terminal branches of the posterior interosseous nerve, which may be compressed, are not easily visible on US.
are shown. The small terminal branches of the posterior interosseous nerve, which may be compressed, are not easily visible on US.