Gastric GIST
R. Brooke Jeffrey, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Submucosal tumor of GI tract derived from interstitial cells of Cajal
Imaging
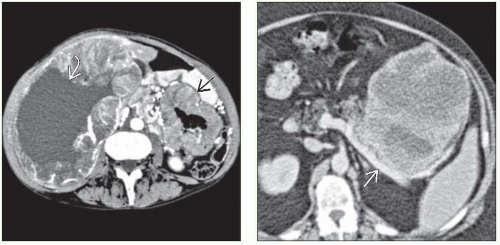
Hypo- or hypervascular, well-circumscribed, submucosal mass on arterial phase images; ulceration and necrosis common on CECT
PET superior to CT in predicting early response to Gleevec
Hypermetabolic foci for both primary tumor and metastases
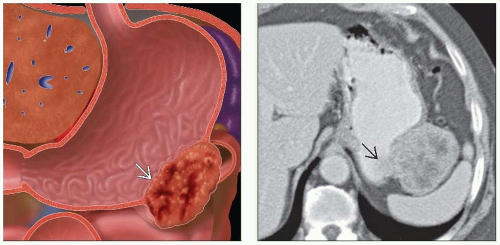
Best diagnostic clue: Well-circumscribed, submucosal mass extending exophytically from GI tract
Best imaging tool: CECT, PET
Nonenhancing necrotic or hemorrhagic areas
Top Differential Diagnoses
Gastric lymphoma
Sarcoma invading stomach
Exophytic gastric carcinoma
Submucosal GI lipoma
Pathology
Distinct, not synonymous with leiomyoma/sarcoma; may not be diagnosed by light microscopy alone
Clinical Issues
Mass effect from bulky tumor; GI bleed when ulcerated; nausea, vomiting, weight loss
Excellent prognosis for completely resected benign lesions
Good response to chemotherapy (Gleevec) in patients with metastatic disease and c-KIT mutation
Prognosis often depends on tumor size
Poor if > 5 cm
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST)
Definitions
Submucosal tumor of gastrointestinal (GI) tract derived from interstitial cells of Cajal
IMAGING
General Features
Best diagnostic clue
Well-circumscribed, submucosal mass extending exophytically from GI tract
Location
Stomach most common site (2/3 of cases)
Small bowel (especially duodenum) 2nd most common site
May occur anywhere in GI tract
Rarely occurs in esophagus (leiomyoma more common)
Size
Variable; large mass may be > 5 cm
Morphology
Bulky, well circumscribed, and lobulated
Often exophytic, may have cystic element
Fluoroscopic Findings
UGI
Rounded, exophytic, submucosal gastric mass
Ulcerations common in larger masses
CT Findings
NECT
Calcifications in 25% of cases
CECT
Hypo- or hypervascular, well-circumscribed, submucosal mass on arterial phase images; ulceration and necrosis common on CECT
Sensitivity (93%), specificity (100%)
MR Findings
T1WI
Isointense mass
T2WI
Hypo- to isointense submucosal mass
Hyperintense areas of necrosis
T2* GRE
Hyper- or hypointense with IV gadolinium
T1WI C+
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree