Presentation
Treatment recommendations
Isolated lateral pelvic recurrences
Resection, palliative EBRT, SBRT, or systemic therapy
Isolated nodal recurrence
Resection, EBRT ± SBRT, SBRT alone, or systemic therapy
Oligometastatic disease
Resection, SBRT, or systemic therapy
Work-Up and Recommended Imaging
H&P, including prior radiotherapy, detailed gynecologic history, performance status , pelvic examination.
Review of systems .
Vaginal bleeding .
Pelvic or back pain .
Neuropathy associated with sidewall recurrences leading to leg pain or weakness.
Bowel or bladder symptoms.
Labs.
CBC , metabolic panel, liver function tests.
Imaging.
MRI within 2 weeks of SBRT .
PET /CT or CT with contrast as alternatives for recurrent disease.
Pathology.
FNA or CT-guided biopsy of accessible lesions.
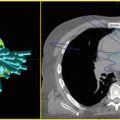
Radiosurgical Technique
Simulation and Treatment Planning
Supine position, arms on chest or overhead.
Immobilization with body frame and/or fiducial or spine tracking .
Thin-cut CT (≤2.5 mm thickness) recommended.
IV and oral contrast to delineate bowel and vessels.
GTV is contoured using fusion of the MRI or PET /CT scan merged into the area of interest on simulation CT scan.
PTV = GTV + 3–8 mm (dependent upon site-specific motion considerations).
Low dose to organs at risk can be achieved using a large number of beam angles and smaller margins.
Phantom-based QA on all treatment plans prior to delivery of first fraction.
Dose Prescription
Doses are divided into 1–5 fractions usually over 1–2 weeks.
SBRT alone in previously un-irradiated sites:
SBRT alone in previously irradiated fields:
SBRT with EBRT 45 Gy for PALN recurrences:
5 Gy × 4–5 fractions (Higginson et al. 2011).
In series where SBRT has substituted for brachytherapy boost during initial treatment of the primary tumor, dose prescriptions mimic commonly accepted brachytherapy schedules.
Dose prescribed to 70–80 % IDL .
Dose Limitations
Dose limitations to normal structures should meet accepted brachytherapy standards or those as outlined in TG-101 (see Appendix).
In the setting of re-irradiation , composite planning should be employed, with appropriate BED conversion for dose summation.
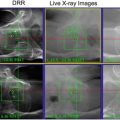
Dose Delivery
Initial verification by kV X-ray or CBCT to visualize the tumor or surrogate markers for positioning.
Verification imaging should be repeated at least every 5 min for longer treatments.
Toxicities and Management
Grade 3 or higher acute toxicity or severe late toxicity is rare.
Common acute toxicities:
Fatigue:
Usually self-limiting but may last for several weeks to months.
Urethritis /cystitis :
Treatment with phenazopyridine or topical analgesics at the urethra .
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree