1
Head and Neck
There will be 14 questions on imaging procedures for the head and neck in the advanced-level examination for MRI. These will cover the following areas
- Brain
- Internal auditory canal
- Pituitary
- Orbit
- Cranial nerves
- Soft tissue – neck
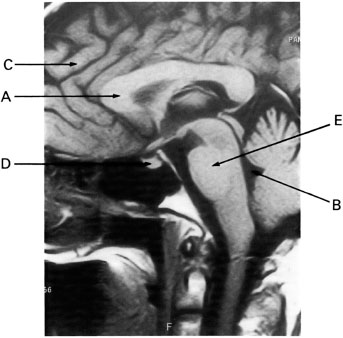
Q1 Image 1 was acquired in the:
| (a) | Axial imaging plane |  |
| (b) | Sagittal imaging plane |  |
| (c) | Coronal imaging plane |  |
| (d) | Off-axis (oblique) imaging plane |  |
Q2 Image 1 is an example of:
| (a) | A T1 weighted image |  |
| (b) | A T2 weighted image |  |
| (c) | A spin (proton) density weighted image |  |
| (d) | None of the above |  |
| (e) | A T2* weighted image |  |
Q3 On image 1, arrow A is pointing to:
| (a) | The corpus callosum |  |
| (b) | The caudate nucleus |  |
| (c) | The internal capsule |  |
| (d) | The lateral ventricle |  |
Q4 On image 1, the tissue indicated by arrow A is made up primarily of:
| (a) | White matter |  |
| (b) | Gray matter |  |
| (c) | Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) |  |
| (d) | Muscle |  |
Q5 On image 1, arrow B is pointing to:
| (a) | The parietal lobe |  |
| (b) | The frontal lobe |  |
| (c) | The internal auditory canals |  |
| (d) | The fourth ventricle |  |
Q6 On image 1, the tissue of the structure marked by arrow B is made up primarily of:
| (a) | White matter |  |
| (b) | Gray matter |  |
| (c) | CSF |  |
| (d) | Muscle |  |
Q7 On image 1, arrow C is pointing to a tissue made up primarily of:
| (a) | White matter |  |
| (b) | Gray matter |  |
| (c) | CSF |  |
| (d) | Muscle |  |
Q8 On image 1, arrow D is pointing to:
| (a) | The caudate nucleus |  |
| (b) | The cerebellar peduncles |  |
| (c) | The internal capsule |  |
| (d) | The pituitary gland |  |
Q9 It is likely that image 1 was acquired with a:
| (a) | Body transmit/receive coil |  |
| (b) | Head transmit/receive coil |  |
| (c) | 5 inch round local or surface receive-only coil |  |
| (d) | Endorectal coil |  |
Q10 On image 1, arrow E is pointing to:
| (a) | The medulla oblongata |  |
| (b) | The pons |  |
| (c) | The spinal cord |  |
| (d) | The mid-brain |  |
Q11 The decreased myelination found in brains of children under one year old results in a lack of image contrast. Consequently, in comparison to scanning adults, to achieve T2 weighted images during pediatric brain imaging often requires a:
| (a) | Longer TE |  |
| (b) | Longer TR |  |
| (c) | Longer TI |  |
| (d) | Higher flip angle |  |
Q12 To optimize brain imaging when evaluating patients for metastatic disease, one FDA approved contrast agent can be administered:
| (a) | With single dose followed by rapid imaging |  |
| (b) | With a triple dose followed by rapid imaging |  |
| (c) | With single dose and imaging followed by twice the dose again after 30 minutes |  |
| (d) | a and b |  |
Q13 With a history of seizures, the patient can be imaged using cardiac gating:
| (a) | To minimize pulsatile flow motion artifact in the temporal lobes |  |
| (b) | To monitor the patient for potential seizures |  |
| (c) | To avoid talking to the patient throughout the study |  |
| (d) | To make vessels appear black |  |
Q14 When patients arrive at the imaging center with a cranial scar, the technologist can:
| (a) |



