8 Hematological Diseases
Plasmocytoma
Definition
Malignant tumor with both multiple and solitary skeletal involvement, characterized by round plasma cell-related cells of different degrees of immaturity, including atypical shapes.
Generalized Plasmocytoma (Multiple Myeloma, Kahler Disease)
Pathology
Diffuse osseous involvement leads to destruction of the spongiosa, producing osteolytic lesion through confluence of initially small defects; later also cortical destruction.
Clinical Findings
 Anemia
Anemia
 Weight loss
Weight loss
 Bone pain
Bone pain
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ Primary method of choice)
(→ Primary method of choice)
Recommended views
 Humerus in two projections
Humerus in two projections
 Low KV technique for high-contrast visualization
Low KV technique for high-contrast visualization
Findings
 Generalized osteoporosis
Generalized osteoporosis
 Osteolytic lesions, usually well-defined and about of equal size
Osteolytic lesions, usually well-defined and about of equal size
 Punched-out cortical defects without periosteal reaction (Fig. 8.1)
Punched-out cortical defects without periosteal reaction (Fig. 8.1)
 (→ Supplementary method)
(→ Supplementary method)
Recommended protocol
 Axial
Axial
 Section thickness: 2 mm
Section thickness: 2 mm
 High-resolution technique
High-resolution technique
Findings
 Coarse bone structure
Coarse bone structure
 Visualization of small osteolytic lesions that are not yet detectable radiographically
Visualization of small osteolytic lesions that are not yet detectable radiographically
 (→ Supplementary method)
(→ Supplementary method)
Recommended section
 Coronal
Coronal
Recommended sequences
 T1-weighted spin-echo (SE)
T1-weighted spin-echo (SE)
Findings
 Patchy hypointensity
Patchy hypointensity
Goals of Imaging
 Determination of decreased bone-mineral density
Determination of decreased bone-mineral density
 Visualization of osteolytic lesions or bone destruction
Visualization of osteolytic lesions or bone destruction
 Visualization of extraosseous tumor component
Visualization of extraosseous tumor component
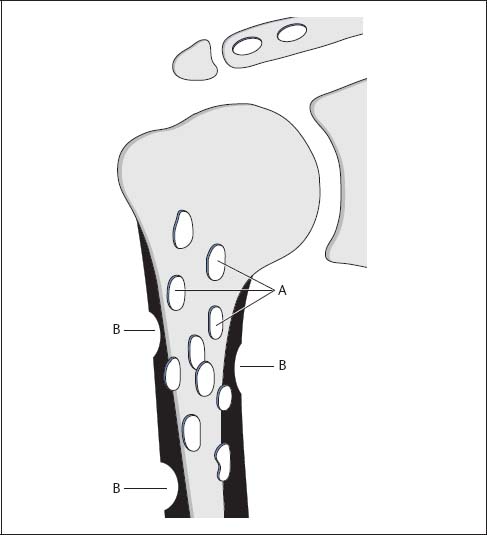
Fig. 8.1  Generalized plasmocytoma
Generalized plasmocytoma
A | Well-defined osteolytic lesions, ranging in size from a few millimeters to several centimeters but all about the same size in the individual patient. |
B | Punched-out cortical defects without periosteal reaction or accompanying soft-tissue changes. |
Disseminated, Nonosteolytic Myelomatosis (Diffusely Demineralizing Myelomatosis)
Pathology
 Generalized bone-marrow involvement
Generalized bone-marrow involvement
 Thinned and rarefied spongiosa
Thinned and rarefied spongiosa
Clinical Findings
 Anemia
Anemia
 Diffuse bone pain
Diffuse bone pain
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ Method of choice)
(→ Method of choice)
Recommended views
 Shoulder in two planes
Shoulder in two planes
Findings
 Diffuse osteoporosis
Diffuse osteoporosis
 Indistinguishable from osteoporosis of other causes
Indistinguishable from osteoporosis of other causes
Therapeutic Principles
 Solitary: Radiation
Solitary: Radiation
 Diffuse: Plasmocytoma-directed chemotherapy, possible osteoclastic inhibitor, such as bisphosphonate and calcitonin
Diffuse: Plasmocytoma-directed chemotherapy, possible osteoclastic inhibitor, such as bisphosphonate and calcitonin
Solitary Plasmocytoma (Solitary Myeloma)
Pathology
 Plasmocytoma confined to a single lesion
Plasmocytoma confined to a single lesion
 Large osteolytic lesion caused by stimulated osteoclasts
Large osteolytic lesion caused by stimulated osteoclasts
Clinical Findings
 Pain
Pain
 Swelling
Swelling
 Possibly spontaneous fracture
Possibly spontaneous fracture
Diagnostic Evaluation
 (→ Primary method of choice)
(→ Primary method of choice)
Recommended views
 Anteroposterior (AP) view of the shoulder and proximal humerus
Anteroposterior (AP) view of the shoulder and proximal humerus
 Axial view of the shoulder and proximal humerus
Axial view of the shoulder and proximal humerus
Findings (Fig. 8.2)
 Sharply demarcated osteolytic defect
Sharply demarcated osteolytic defect
 Cortical destruction
Cortical destruction
 Expansion of the bone due to neocortex
Expansion of the bone due to neocortex
 No calcifications within the tumor
No calcifications within the tumor
 (→ Supplementary method)
(→ Supplementary method)
Recommended protocol
 Standard axial sections
Standard axial sections
 Possibly coronal reconstruction
Possibly coronal reconstruction
Findings
 Osteolytic tumor
Osteolytic tumor
 Neocortex
Neocortex
 Tumor breakthrough with paraosseous component
Tumor breakthrough with paraosseous component
 (→ Supplementary method)
(→ Supplementary method)
Recommended sections
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


